Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 21 Sept 2024
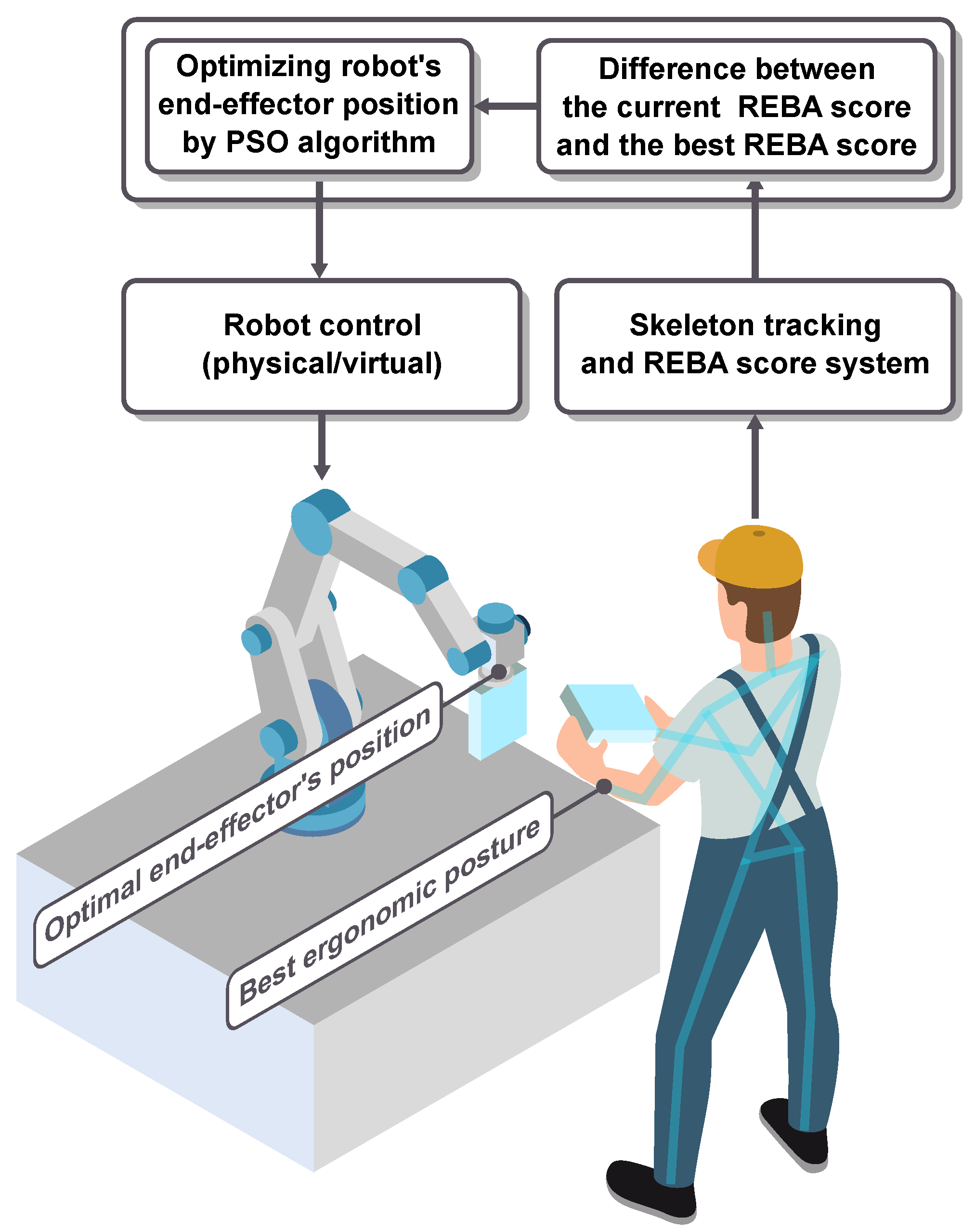
Musculoskeletal disorders caused by poor work posture are a serious concern in the industry since they lead to absenteeism and medical leave from work. In the context of human–robot collaboration, this issue can be mitigated if collaborative robots support human workers to perform their tasks more ergonomically. In this work, we propose a method to optimize human posture during human–robot collaboration using the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm. Our approach involves assigning an appropriate location to the robot’s end-effector to minimize the distance between the optimized posture of the human and their current posture in the working space. To measure human posture, we use the Rapid Entire Body Assessment score (REBA) calculated from body joint angles captured by a Kinect camera. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, we conducted a user study with 20 participants in a virtual reality environment. The PSO algorithm could position the robot end-effector to the optimal position close to real time. Our results showed that our method could improve ergonomics by 66%, indicating its potential for use in human–robot collaborative applications.
Applied Science & Technology Full Text
Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, press fit
Academic applied science-technology-full-text
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, press f to respect significado
New WoS July 22 Release Notes - Web of Science Group
S. Chand's Applied Science Polytechnic II Sem.: Dilip Gaikkwad: 9788121934664: : Books
Introduction to libre « fulltext » technology
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, script king legacy mobile sem key
Home Discover Applied Sciences
Recommended for you
 Posture Correcting Bra14 Jul 2023
Posture Correcting Bra14 Jul 2023 Post-Surgery Closure Bra for Women Posture Corrector Compression14 Jul 2023
Post-Surgery Closure Bra for Women Posture Corrector Compression14 Jul 2023 Sursell Posture Correction Front-Close Bra,Women's Full Coverage Front Closure Support Bra14 Jul 2023
Sursell Posture Correction Front-Close Bra,Women's Full Coverage Front Closure Support Bra14 Jul 2023 Open and closed posture. Download Scientific Diagram14 Jul 2023
Open and closed posture. Download Scientific Diagram14 Jul 2023 Front Closing Bras - Shop Front Closing Bras Australia Wide - Curvy14 Jul 2023
Front Closing Bras - Shop Front Closing Bras Australia Wide - Curvy14 Jul 2023 Front Close Soft Cup Posture Bra14 Jul 2023
Front Close Soft Cup Posture Bra14 Jul 2023 Ortho Active Posture Corrector Front Closure14 Jul 2023
Ortho Active Posture Corrector Front Closure14 Jul 2023 Women's Full Coverage Non-padded Wire Free Front Closure Posture Bra Plus Size X Bcak Plus Size 46 48 D E F G - AliExpress14 Jul 2023
Women's Full Coverage Non-padded Wire Free Front Closure Posture Bra Plus Size X Bcak Plus Size 46 48 D E F G - AliExpress14 Jul 2023 Fotografia do Stock: adult male with a beard. isolated on white background. Closed posture. arms and legs crossed. body language14 Jul 2023
Fotografia do Stock: adult male with a beard. isolated on white background. Closed posture. arms and legs crossed. body language14 Jul 2023 Critical Timing to Break Opponent's Posture from Closed Guard - Fabio Gurgel14 Jul 2023
Critical Timing to Break Opponent's Posture from Closed Guard - Fabio Gurgel14 Jul 2023
You may also like
 Beautiful Vintage 1970s Gingham Square Dancing Dress Size 8 / 1014 Jul 2023
Beautiful Vintage 1970s Gingham Square Dancing Dress Size 8 / 1014 Jul 2023 Realistic Paper Clip Office Metal Black Binder Clip Paper Holder14 Jul 2023
Realistic Paper Clip Office Metal Black Binder Clip Paper Holder14 Jul 2023 Sizing Charts: Jill Wolcott Knits Size Chart XS to XL14 Jul 2023
Sizing Charts: Jill Wolcott Knits Size Chart XS to XL14 Jul 2023- Bombshell Victoria Secret Push Up bra 32C 70C C70 C32, Women's14 Jul 2023
 Achi Village Peach Blossom Festival 2024 - Events in Nagano14 Jul 2023
Achi Village Peach Blossom Festival 2024 - Events in Nagano14 Jul 2023 PSD x Rick and Morty Wash Boxer Briefs14 Jul 2023
PSD x Rick and Morty Wash Boxer Briefs14 Jul 2023 Spyder – Skiis & Biikes14 Jul 2023
Spyder – Skiis & Biikes14 Jul 2023 Isdinceutics Isdin Skin Drops Sand Arena Maquillaje14 Jul 2023
Isdinceutics Isdin Skin Drops Sand Arena Maquillaje14 Jul 2023- Red Robe Mens : Target14 Jul 2023
 LuLu-B Hearts 1/4 Zip – Lake Effect14 Jul 2023
LuLu-B Hearts 1/4 Zip – Lake Effect14 Jul 2023