Assessment of Obstetric Risk Factors for Postpartum Urinary Retention After Vaginal Delivery: A Case-Control Study, PDF, Childbirth
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 20 Sept 2024

Jurnal - Postpartum Urinary Retention - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This study assessed risk factors for postpartum urinary retention (PPUR) after vaginal delivery in 234 women. PPUR was defined as a postvoid residual bladder volume ≥150 mL or inability to void within 6 hours of delivery. 19 women (8.1%) developed PPUR. Logistic regression found prolonged second stage of labor, episiotomy, perineal laceration, and birth weight >4000g were independent risk factors for PPUR. The study aims to identify women at risk to prevent PPUR and complications.
10.1007@s00192 020 04378 2 PDF, PDF, Childbirth
Covert postpartum urinary retention: causes and consequences
Medicina, Free Full-Text
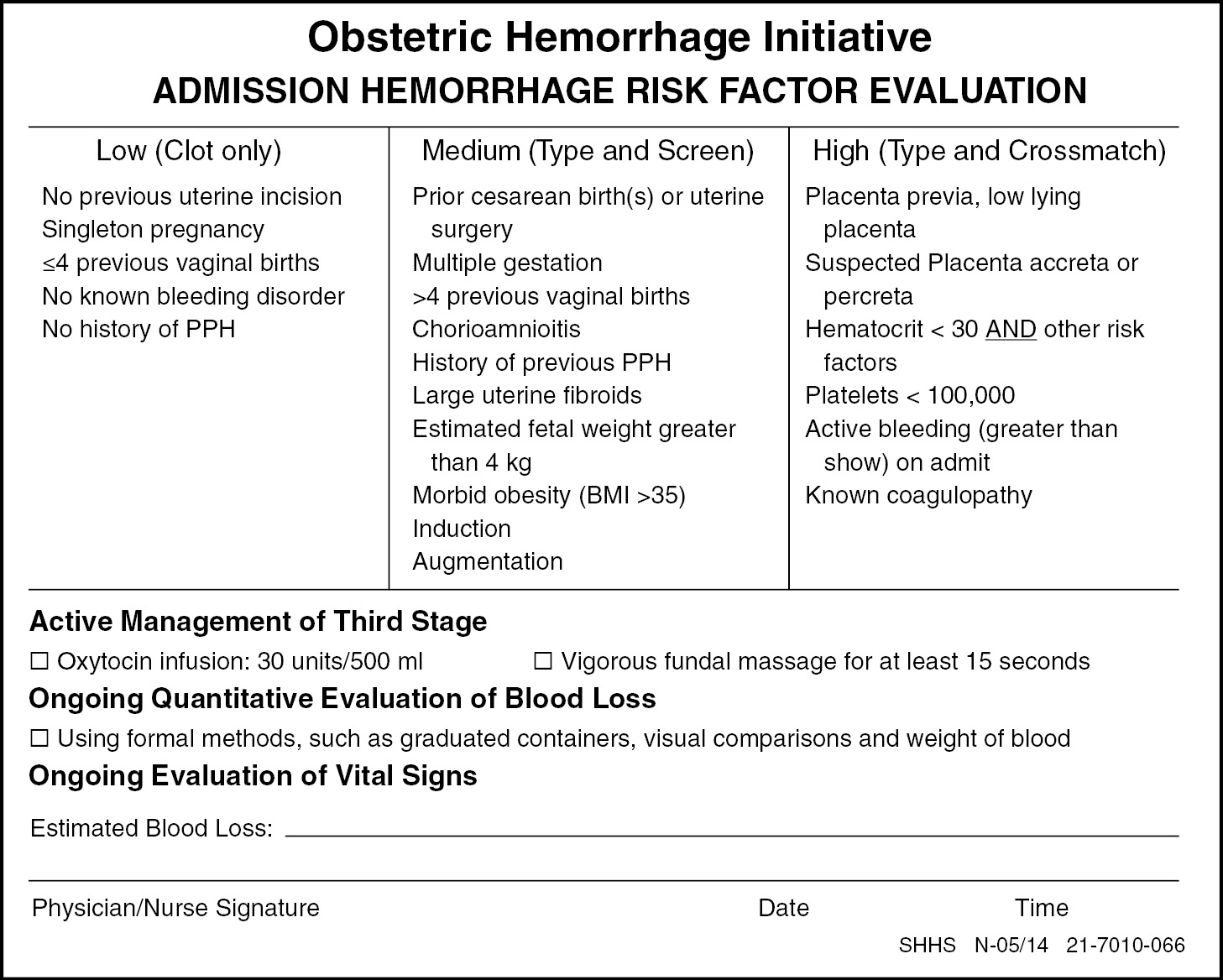
Postpartum Hemorrhage (Chapter 28) - Obstetric Care
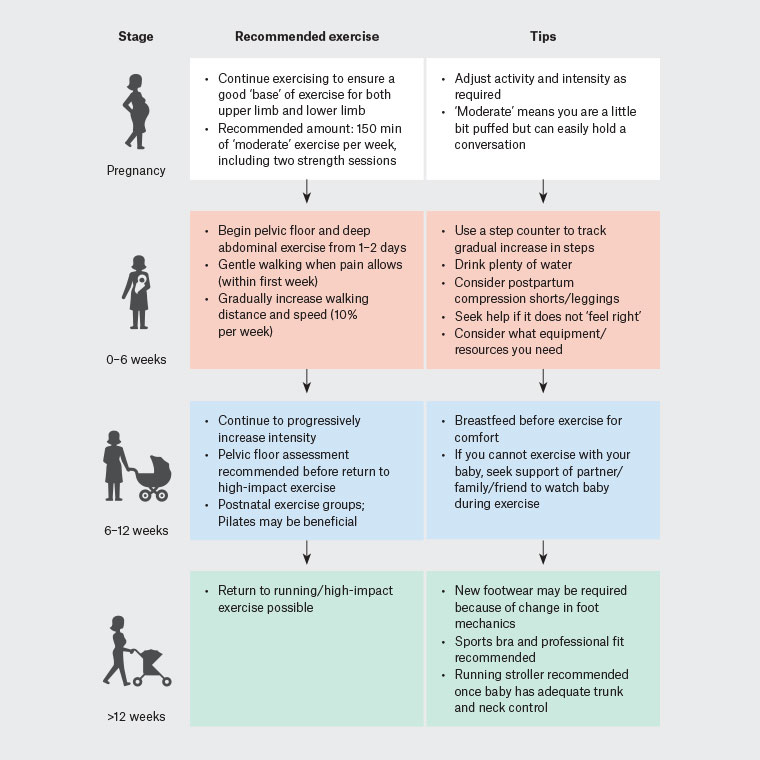
RACGP - Exercise after pregnancy
High-Risk Pregnancy: Nursing Care Management
PDF) Prevalence and factors of urinary incontinence among
Nutrients, Free Full-Text
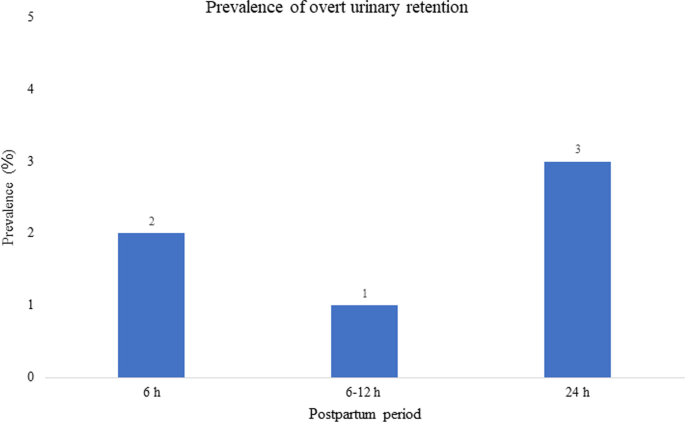
Prevalence of urinary retention after vaginal delivery: a
PDF) Prolonged Postpartum Persistent Urinary Retention After
Analgesia and Anesthesia for the Obstetric Patient by
(PDF) Prevalence and risk factors of overt postpartum urinary
The prevalence of uterine fundal pressure during the second stage
Risk Factors For Postpartum Urinary Retention: A Systematic
Recommended for you
 The risk factors of postpartum urinary retention after vaginal delivery: A systematic review14 Jul 2023
The risk factors of postpartum urinary retention after vaginal delivery: A systematic review14 Jul 2023 Imperial college healthcare protocol14 Jul 2023
Imperial college healthcare protocol14 Jul 2023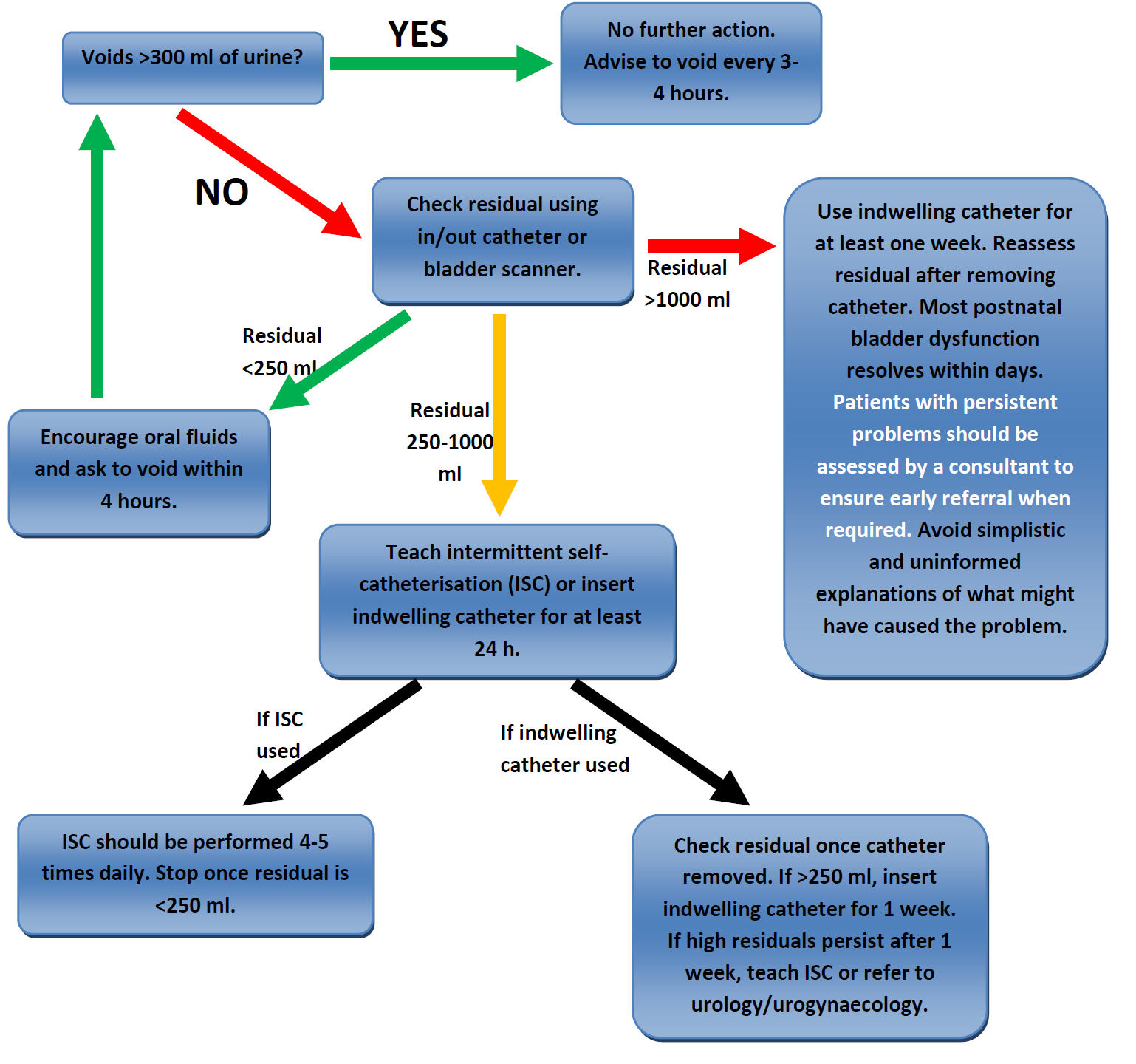 Postnatal Bladder Care (373)14 Jul 2023
Postnatal Bladder Care (373)14 Jul 2023![Postpartum Urinary Retention [+ Free Cheat Sheet]](https://cdn.lecturio.com/assets/Nursing_CS_Postpartum_Urinary_Retention.jpg) Postpartum Urinary Retention [+ Free Cheat Sheet]14 Jul 2023
Postpartum Urinary Retention [+ Free Cheat Sheet]14 Jul 2023 Nurses Drive Initiative to Address Postpartum Urinary Retention14 Jul 2023
Nurses Drive Initiative to Address Postpartum Urinary Retention14 Jul 2023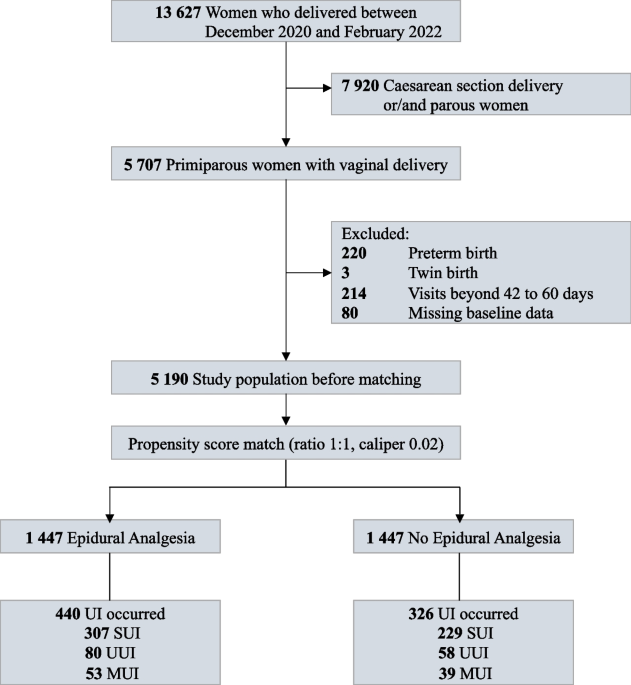 Association of epidural analgesia during labor and early postpartum urinary incontinence among women delivered vaginally: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study, BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth14 Jul 2023
Association of epidural analgesia during labor and early postpartum urinary incontinence among women delivered vaginally: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study, BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth14 Jul 2023 Urine Retention14 Jul 2023
Urine Retention14 Jul 2023 Evaluation and Management of Voiding Dysfunction and Urinary14 Jul 2023
Evaluation and Management of Voiding Dysfunction and Urinary14 Jul 2023 Urinary catheterization in labour with high-dose vs mobile14 Jul 2023
Urinary catheterization in labour with high-dose vs mobile14 Jul 2023 PPT - Postoperative urinary retention PowerPoint Presentation14 Jul 2023
PPT - Postoperative urinary retention PowerPoint Presentation14 Jul 2023
You may also like
- Out From Under Modern Love Corset In Turquoise | ModeSens14 Jul 2023
 Bralette and High Waist Panty – Imperfect14 Jul 2023
Bralette and High Waist Panty – Imperfect14 Jul 2023 Delimira Women's Front Fastening Bra Racer Back Palestine14 Jul 2023
Delimira Women's Front Fastening Bra Racer Back Palestine14 Jul 2023 ELEVATE LEGGINGS - LIGHT VIOLET14 Jul 2023
ELEVATE LEGGINGS - LIGHT VIOLET14 Jul 2023 Curvy Couture Women's Plus Size Beautiful Bliss Lace Unlined Bra14 Jul 2023
Curvy Couture Women's Plus Size Beautiful Bliss Lace Unlined Bra14 Jul 2023 New Sexy Push-up Bra and Panty Sets Beauty Back Closure Lingerie Set Wireless Bras Sexy Lace Lingerie Set Women Deep V Brassiere - AliExpress14 Jul 2023
New Sexy Push-up Bra and Panty Sets Beauty Back Closure Lingerie Set Wireless Bras Sexy Lace Lingerie Set Women Deep V Brassiere - AliExpress14 Jul 2023 Victorian Aristocrat (men's victorian clothing) - For costume tutorials, clothing guide, fashion inspirat…14 Jul 2023
Victorian Aristocrat (men's victorian clothing) - For costume tutorials, clothing guide, fashion inspirat…14 Jul 2023 B&C ID.003 Cotton Rich14 Jul 2023
B&C ID.003 Cotton Rich14 Jul 2023 Teenager Clothes14 Jul 2023
Teenager Clothes14 Jul 2023 WOMEN'S EXTRA STRETCH MATERNITY JEANS14 Jul 2023
WOMEN'S EXTRA STRETCH MATERNITY JEANS14 Jul 2023