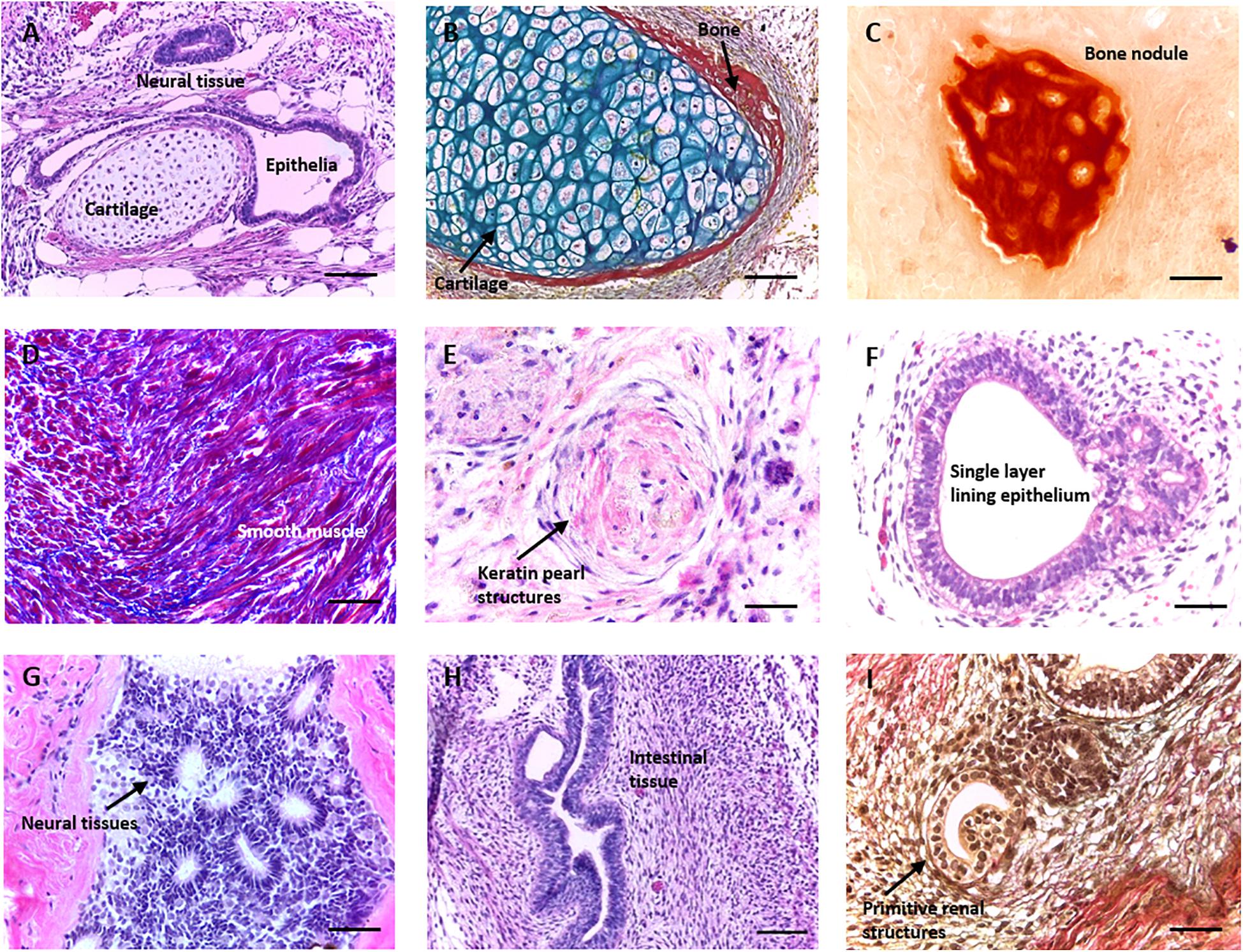
Figure 1, The steps of regenerative medicine. - StemBook - NCBI
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 20 Sept 2024

The production of cellular therapies requires the optimization of four steps: first, isolating and culturing cells that can be readily obtained from a patient in a non-invasive fashion. Second, the reprogramming of these cells into a pluripotent state. Third, the directed differentiation of those patient-specific pluripotent cells into the cell type relevant to their disease. And, fourth, techniques for repairing any intrinsic disease-causing genetic defects and transplantation of the repaired, differentiated cells into the patient. Notably, these disease-relevant patient cells can also be used for in vitro disease modeling which may yield new insights into disease mechanisms and drug discovery.
/content/biorxiv/early/2021/01/21/2
A roundtable on responsible innovation with autologous stem cells
Figure 1, Retention versus stress-induced mobilization of HSPCs
Frontiers Using Advanced Cell Culture Techniques to
Lineage analysis of stem cells - StemBook - NCBI Bookshelf
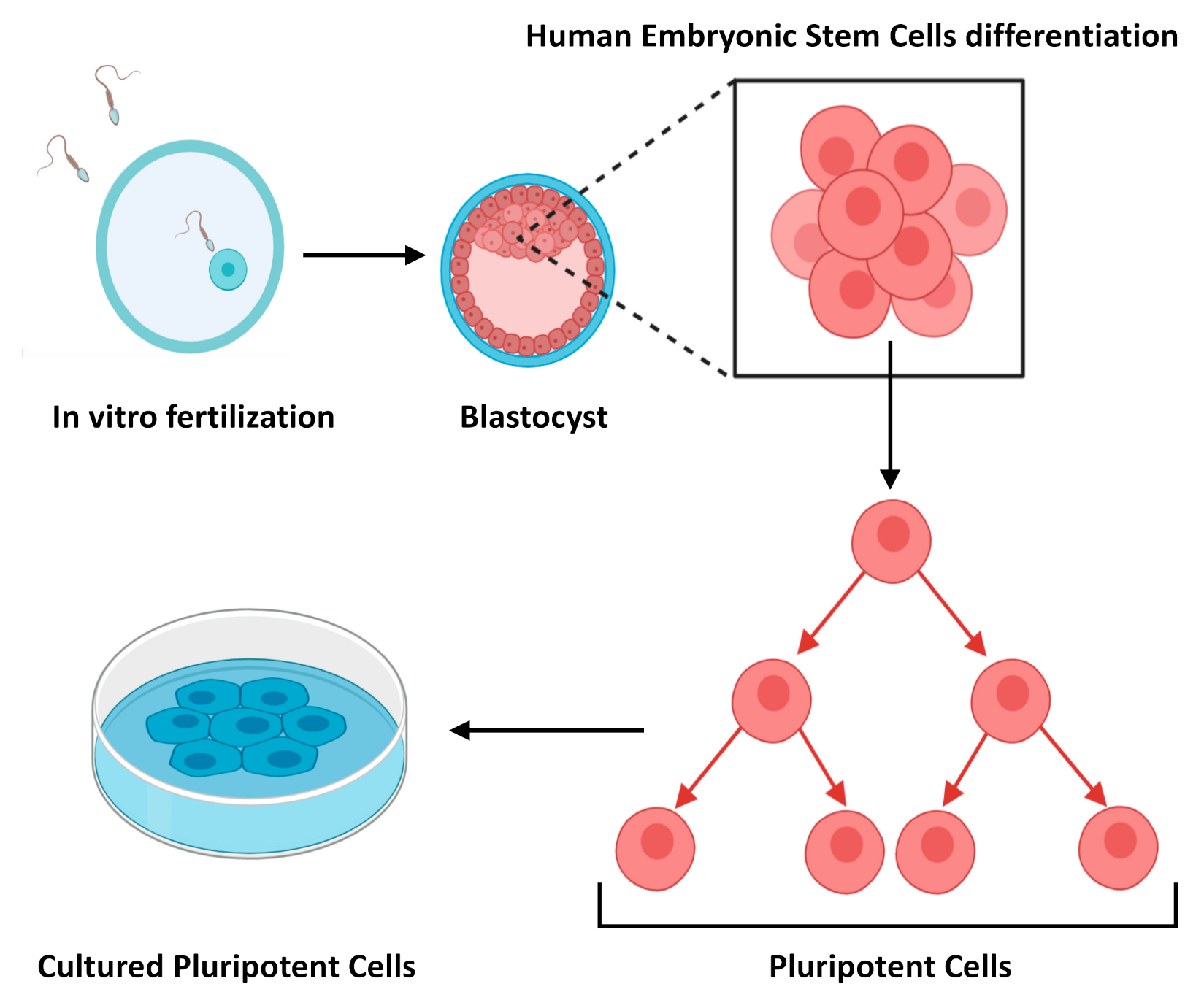
Figure 1, Life cycle of a pluripotent stem cell line. - StemBook
Immunological considerations for cell therapy using human
Formation of embryoid bodies from Matrigel dots protocol
Differential role of natural killer group 2D in recognition and
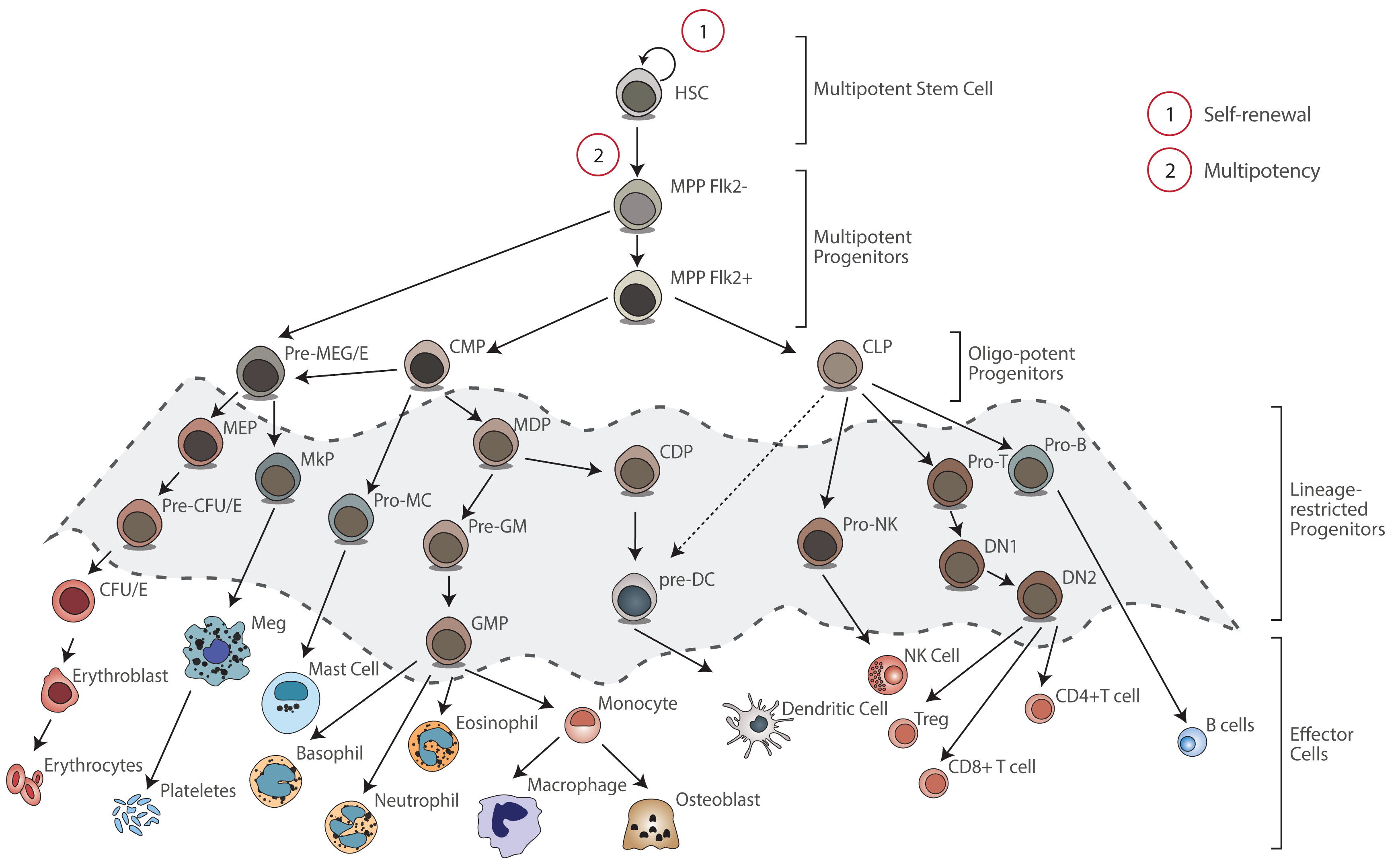
Hematopoietic differentiation - StemBook - NCBI Bookshelf
IJMS, Free Full-Text
PDF) Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering: Advancements
Molecules, Free Full-Text
Age-dependent structural and morphological changes of the stem
Basic pluripotent stem cell culture protocols - StemBook - NCBI
Recommended for you
 Blood Regeneration Blood Reprogramming Technologies14 Jul 2023
Blood Regeneration Blood Reprogramming Technologies14 Jul 2023- The many fates of tissue regeneration14 Jul 2023
 Using stem cells for liver regeneration - Medicine by Design14 Jul 2023
Using stem cells for liver regeneration - Medicine by Design14 Jul 2023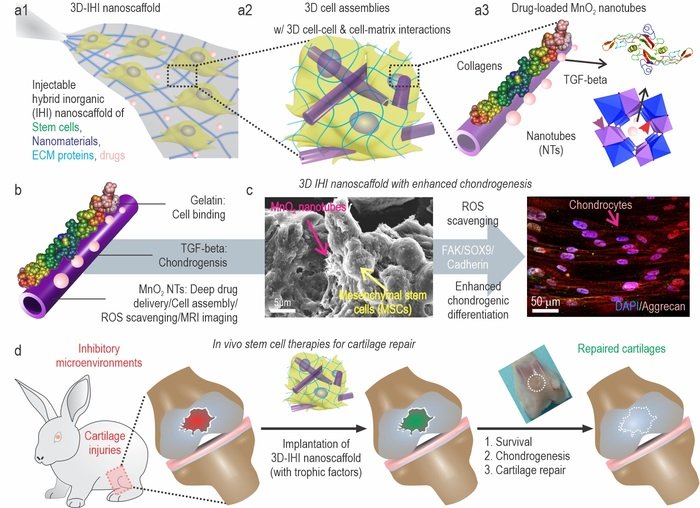 Injectable stem cell assembly for cartilage regeneration •14 Jul 2023
Injectable stem cell assembly for cartilage regeneration •14 Jul 2023 Study uncovers the secrets of plant regeneration14 Jul 2023
Study uncovers the secrets of plant regeneration14 Jul 2023 Scientists Identify How a Biological Pathway Leads Stem Cells to14 Jul 2023
Scientists Identify How a Biological Pathway Leads Stem Cells to14 Jul 2023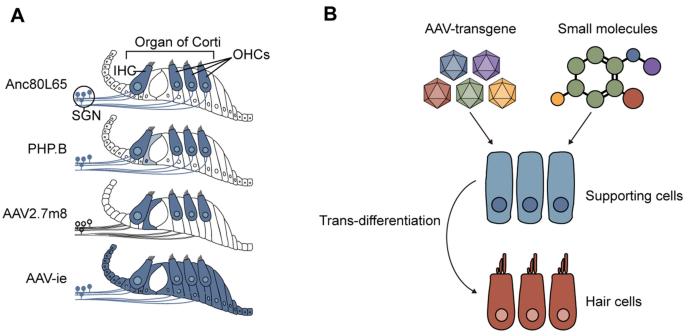 Stem Cell-Based Hair Cell Regeneration and Therapy in the Inner14 Jul 2023
Stem Cell-Based Hair Cell Regeneration and Therapy in the Inner14 Jul 2023 Stem Cell 100+: Multi-Pathway Anti-Aging14 Jul 2023
Stem Cell 100+: Multi-Pathway Anti-Aging14 Jul 2023 CellR4 - Cellular repair, replacement, regeneration, reprogramming14 Jul 2023
CellR4 - Cellular repair, replacement, regeneration, reprogramming14 Jul 2023 Tissue regeneration: Impact of sleep on stem cell regenerative capacity - ScienceDirect14 Jul 2023
Tissue regeneration: Impact of sleep on stem cell regenerative capacity - ScienceDirect14 Jul 2023
You may also like
- Boys' Adventure Shorts - All In Motion™ Olive Green XS14 Jul 2023
 Soma, Intimates & Sleepwear14 Jul 2023
Soma, Intimates & Sleepwear14 Jul 2023 Plus Size Christmas Party Pajamas Set Women's Plus - Temu Canada14 Jul 2023
Plus Size Christmas Party Pajamas Set Women's Plus - Temu Canada14 Jul 2023 Woman's Cornflower Blue Fitness full-zip fleece sweatshirt with hood14 Jul 2023
Woman's Cornflower Blue Fitness full-zip fleece sweatshirt with hood14 Jul 2023 Women Silver Elyse Platforms14 Jul 2023
Women Silver Elyse Platforms14 Jul 2023 Free Woman Whipped Porn Videos (253)14 Jul 2023
Free Woman Whipped Porn Videos (253)14 Jul 2023 Women's Latest Nylon Spandex Seamless Tummy Control high Waist Thigh Ladies Shapewear Half Body Shaper(PACKOF2)14 Jul 2023
Women's Latest Nylon Spandex Seamless Tummy Control high Waist Thigh Ladies Shapewear Half Body Shaper(PACKOF2)14 Jul 2023 SHAPERMINT Bra for Women Supportive Comfortable Seamless - Import It All14 Jul 2023
SHAPERMINT Bra for Women Supportive Comfortable Seamless - Import It All14 Jul 2023 Wake up ready for the day Trendy workout outfits, Fitness14 Jul 2023
Wake up ready for the day Trendy workout outfits, Fitness14 Jul 2023- BDG High-Rise Cropped Kick Flare Jean – Dark Wash14 Jul 2023