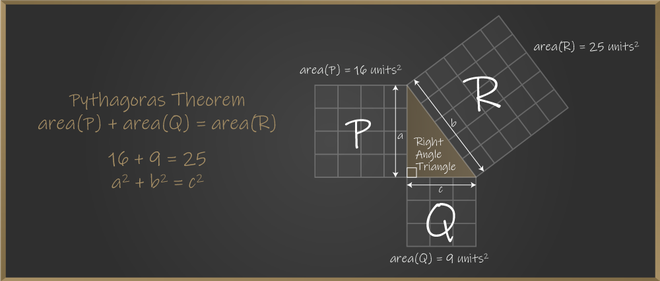
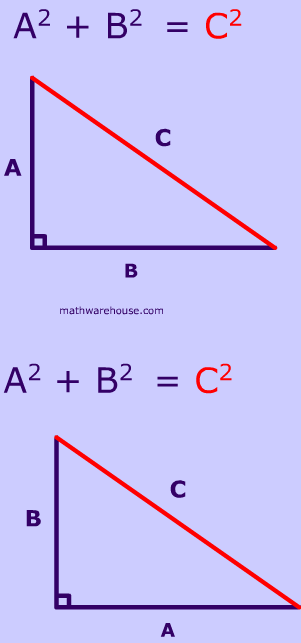
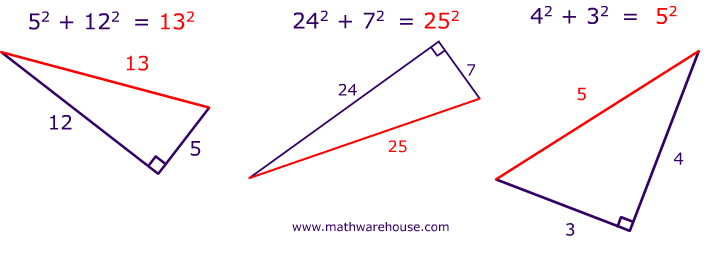
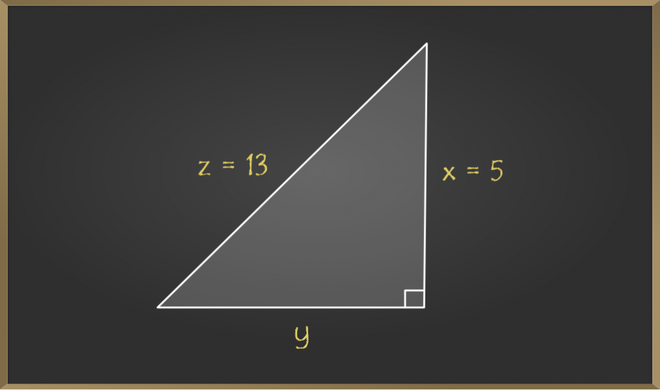How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 21 Sept 2024
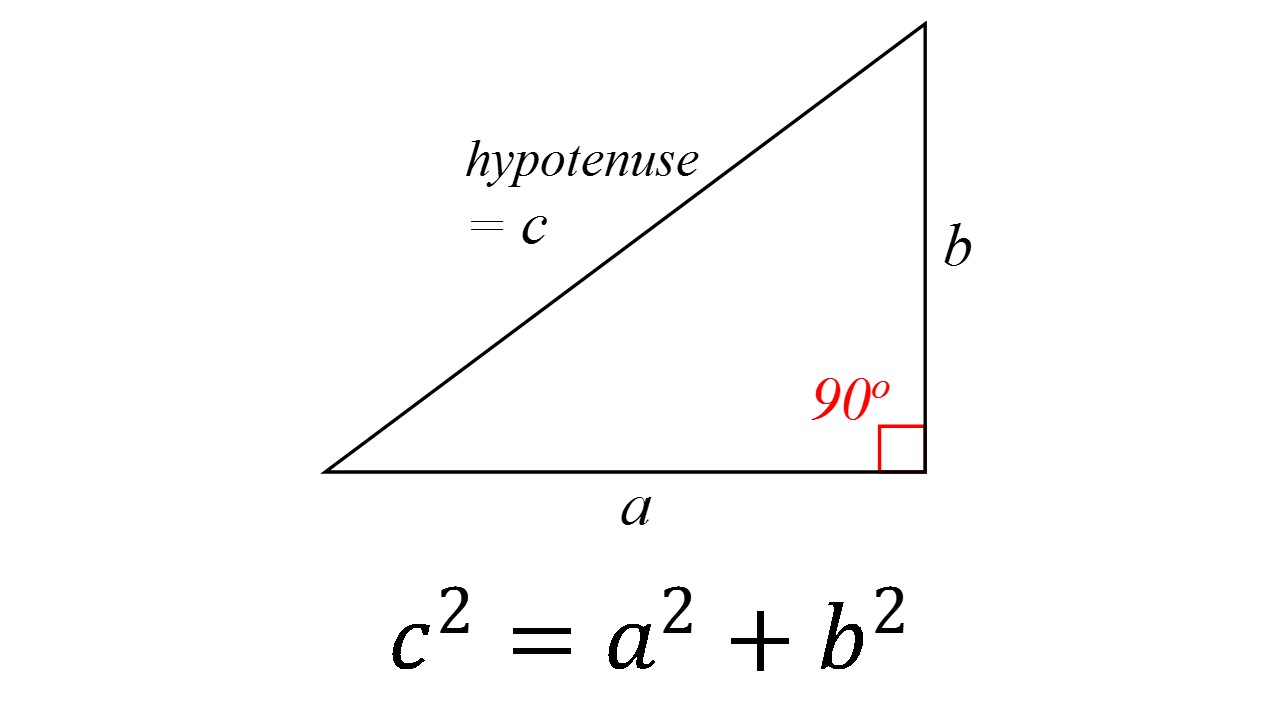
c^2 != a^2 + b^2, therefore, this cannot be a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem applies to right angle triangles, where the sides a and b are those which intersect at right angle. The third side, the hypotenuse, is then c To test whether the given lengths of sides create a right triangle, we need to substitute them into the Pythagorean Theorem - if it works out then it is a right angle triangle: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 15^2 != 5^2+10^2 225 != 25+100 225 != 125 In reality, if a=5 and b=10 then c would have to be c^2 = 125 c =sqrt(125) = 5sqrt(5)~= 11.2 which is smaller than the proposed value in the question. Therefore, this cannot be a right triangle.
How to Use Pythagorean Theorem Converse: Is This a Right Triangle? - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics
Identifying right-angled triangles - Pythagoras' theorem - CCEA - GCSE Maths Revision - CCEA - BBC Bitesize
Pythagoras Theorem Formula, Proof, Examples and Applications
How to Use the Pythagorean Theorem. Step By Step Examples and Practice
Ex: Determine the Distance Between Two Points Using the Pythagorean Theorem
How to Find the Area of a Right Triangle Using the Pythagorean Theorem, Geometry
Pythagoras Theorem Formula, Proof, Examples and Applications
Using the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem Practice, Algebra Practice Problems
Is there a way of finding the hypotenuse of a right angle triangle without using the Pythagorean theorem? - Quora
How to Use the Pythagorean Theorem. Step By Step Examples and Practice
Lesson Explainer: Pythagorean Inequality Theorem
Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem
Recommended for you
- Right triangle trigonometry, Lesson (article)14 Jul 2023
 How to Solve a Right Triangle, Geometry14 Jul 2023
How to Solve a Right Triangle, Geometry14 Jul 2023- Solving Right Triangles14 Jul 2023
 What are Special Right Triangles? Explanation & Examples14 Jul 2023
What are Special Right Triangles? Explanation & Examples14 Jul 2023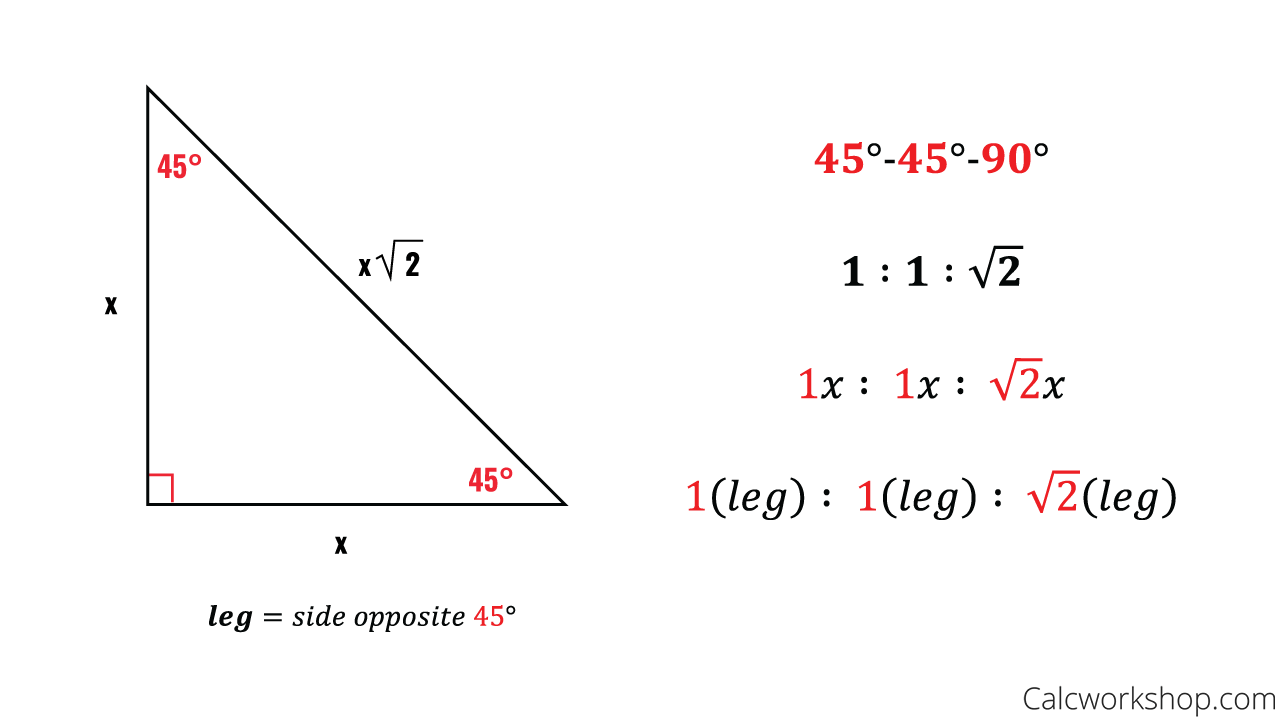 Special Right Triangles (Fully Explained w/ 19 Examples!)14 Jul 2023
Special Right Triangles (Fully Explained w/ 19 Examples!)14 Jul 2023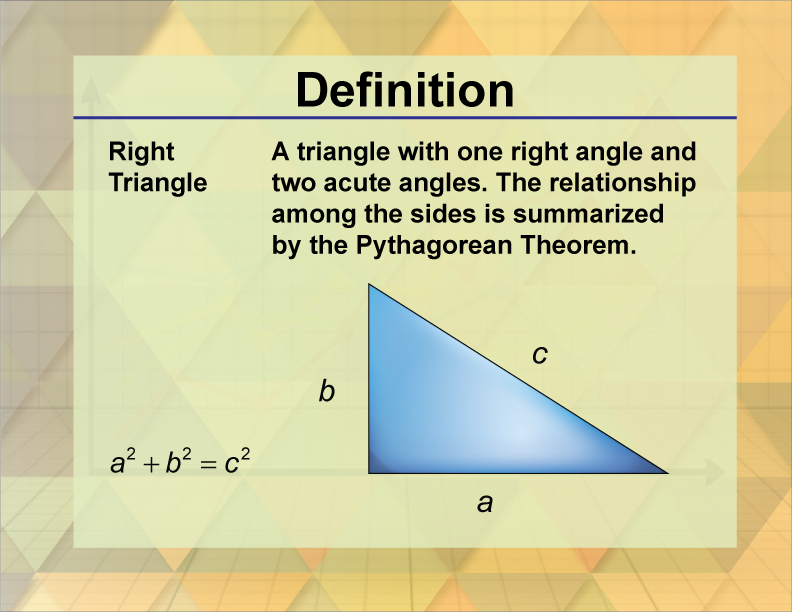 Definition--Triangle Concepts--Right Triangle14 Jul 2023
Definition--Triangle Concepts--Right Triangle14 Jul 2023 Non-right Triangles: Law of Cosines14 Jul 2023
Non-right Triangles: Law of Cosines14 Jul 2023 How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the following triangle with sides a, b, & c is a right triangle: a=5, b=10, c=15?14 Jul 2023
How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the following triangle with sides a, b, & c is a right triangle: a=5, b=10, c=15?14 Jul 2023 Perimeter of a Right Triangle Formula, Methods & Examples14 Jul 2023
Perimeter of a Right Triangle Formula, Methods & Examples14 Jul 2023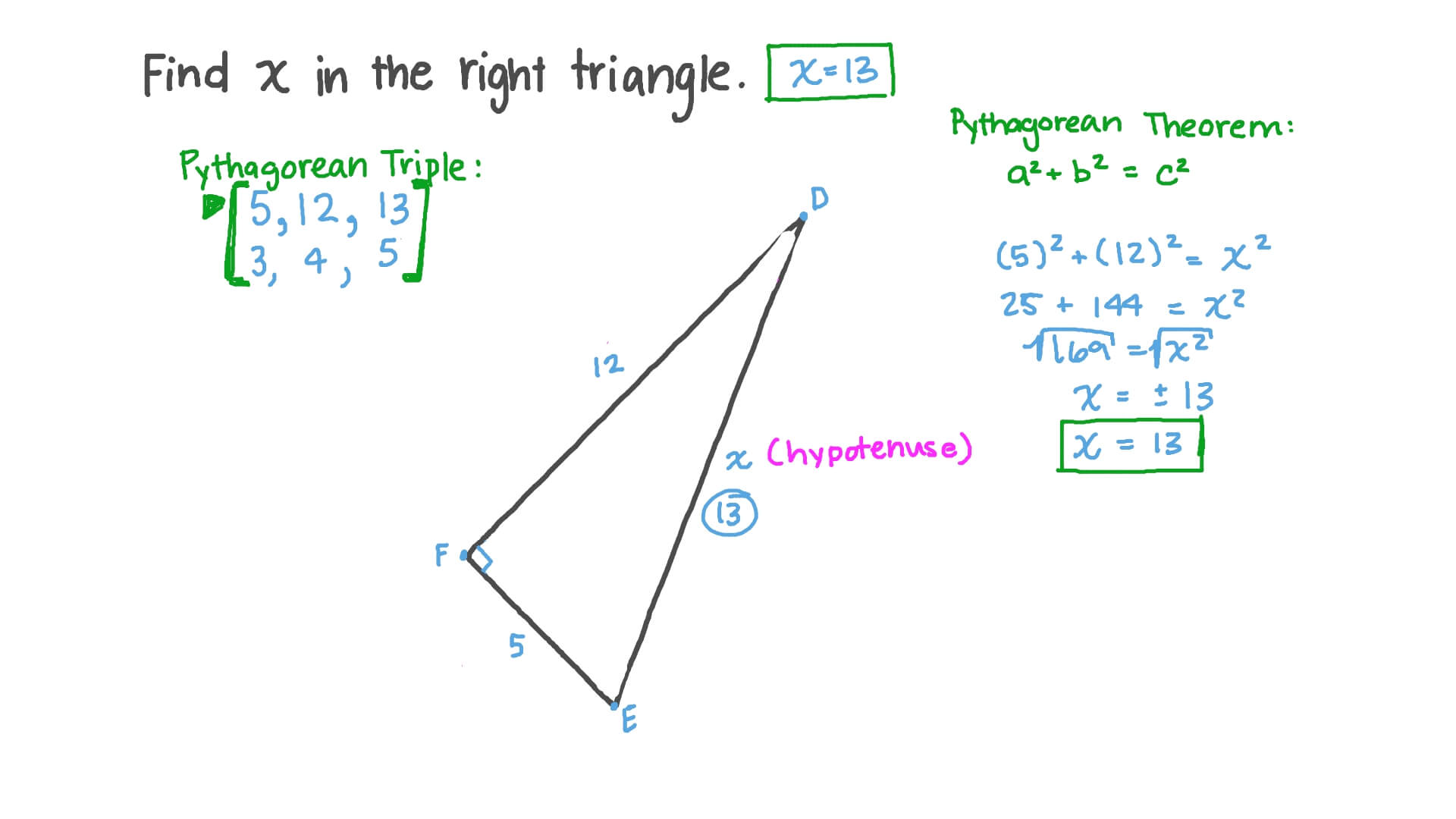 Question Video: Solving for the Hypotenuse of a Right Triangle14 Jul 2023
Question Video: Solving for the Hypotenuse of a Right Triangle14 Jul 2023
You may also like
 Figure My Hero Academia- All Might Coleção - Banpresto Figure14 Jul 2023
Figure My Hero Academia- All Might Coleção - Banpresto Figure14 Jul 2023 Women's Black Southern Indiana Screaming Eagles Plus Size Thigh Logo Yoga Leggings14 Jul 2023
Women's Black Southern Indiana Screaming Eagles Plus Size Thigh Logo Yoga Leggings14 Jul 2023- Bali Women's Double Support Wire-free Bra - 3820 38c Blue Sky Ahead : Target14 Jul 2023
 TS GENCO AE Offline Mega Mock Tests (ECE, EEE, CE, ME)14 Jul 2023
TS GENCO AE Offline Mega Mock Tests (ECE, EEE, CE, ME)14 Jul 2023 LIVI Sports Bra Black 46C Wireless Medium-Impact Wicking14 Jul 2023
LIVI Sports Bra Black 46C Wireless Medium-Impact Wicking14 Jul 2023 Fabletics Womens Ines Sports Bra Low Impact Corset Stitching Hook and Eye XS/414 Jul 2023
Fabletics Womens Ines Sports Bra Low Impact Corset Stitching Hook and Eye XS/414 Jul 2023 Guitarra Waldman Strato Vermelha St-111 Rd (8457)14 Jul 2023
Guitarra Waldman Strato Vermelha St-111 Rd (8457)14 Jul 2023 Kids Kaftan by Pattern Emporium — Pattern Revolution14 Jul 2023
Kids Kaftan by Pattern Emporium — Pattern Revolution14 Jul 2023 Rare Vintage 1992 Easyriders Skull Harley Motorcycle T-shirt14 Jul 2023
Rare Vintage 1992 Easyriders Skull Harley Motorcycle T-shirt14 Jul 2023 Wolford Olaf Hajek Tights For Women at Women's Clothing store14 Jul 2023
Wolford Olaf Hajek Tights For Women at Women's Clothing store14 Jul 2023