Associations of body shapes with insulin resistance and
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 24 Sept 2024
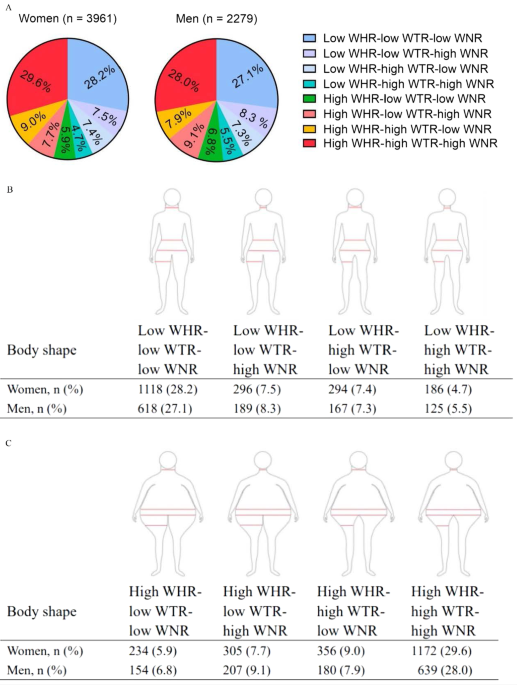
Background We aimed to define refined body shapes by using multiple anthropometric traits that represent fat distribution, and evaluate their associations with risk of insulin resistance (IR) and cardiometabolic disorders in a Chinese population. Methods We performed a cross-sectional analysis in 6570 community-based participants aged ≥ 40 years. Four body circumferences (neck, waist, hip, and thigh) and their ratios were put simultaneously into an open-source Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis platform to select the worthiest indicators in determining IR. The ratio of the top 3 fat distribution indicators was used to define the refined body shapes. Results We defined 8 distinct body shapes based on sex-specific combinations of waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), waist-to-thigh ratio (WTR), and waist-to-neck ratio (WNR), which differed in participants’ distribution and risk of IR and related cardiometabolic disorders. In women, as compared to the low WHR-low WTR-low WNR shape, all body shapes were significantly associated with IR and related cardiometabolic disorders; while in men, the low WHR-high WTR-high WNR shape and the higher WHR related shapes were significantly associated with IR and related cardiometabolic disorders. Stratified by WHR, the results were consistent in women; however, no significant associations were detected in men. Conclusions We defined 8 distinct body shapes by taking WHR, WTR, and WNR, simultaneously into account, which differed in association with the risk of IR and related cardiometabolic disorders in women. This study suggests that body shapes defined by multiple anthropometric traits could provide a useful, convenient, and easily available method for identifying cardiometabolic risk.
PDF) Insulin resistance and associated factors: A cross-sectional study of bank employees
PDF) Neck Circumference and the Development of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in the Framingham Heart Study
Yuhong Chen's research works Ruijin Hospital North, Shanghai and other places
The prevalence of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome according
PDF) The role of insulin resistance in the relation of visceral, abdominal subcutaneous and total body fat to cardiovascular function
Evaluation of polygenic risk models using multiple performance measures: a critical assessment of discordant results
PDF) New clusters of serum electrolytes aid in stratification of diabetes and metabolic risk
Performance of RunEntropy biomarkers for the diagnosis of MetS (a) and
Age-standardised mean BMI and WHR measures (a) and serum lipids (b) in
PDF) Associations of body shapes with insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk in middle-aged and elderly Chinese
Association of MED Intake With Incident Type 2 Diabetes After
Diabetes and Endocrine Function
Age-standardised mean BMI and WHR measures (a) and serum lipids (b) in
Recommended for you
 Personal stylist tips: Apple body shape styling14 Jul 2023
Personal stylist tips: Apple body shape styling14 Jul 2023 Dealing With The Average Body Type14 Jul 2023
Dealing With The Average Body Type14 Jul 2023 The average man has a six pack : r/BadMensAnatomy14 Jul 2023
The average man has a six pack : r/BadMensAnatomy14 Jul 2023 Average Man Body: Over 379 Royalty-Free Licensable Stock Illustrations & Drawings14 Jul 2023
Average Man Body: Over 379 Royalty-Free Licensable Stock Illustrations & Drawings14 Jul 2023 What is Body Type?14 Jul 2023
What is Body Type?14 Jul 2023 Frontiers An Assessment of Computer-Generated Stimuli for Use in Studies of Body Size Estimation and Bias14 Jul 2023
Frontiers An Assessment of Computer-Generated Stimuli for Use in Studies of Body Size Estimation and Bias14 Jul 2023- How the 'Perfect' Male Body Has Changed14 Jul 2023
 Body shape expectations and self-ideal body shape discrepancy in women seeking bariatric surgery: a cross-sectional study, BMC Obesity14 Jul 2023
Body shape expectations and self-ideal body shape discrepancy in women seeking bariatric surgery: a cross-sectional study, BMC Obesity14 Jul 2023 Associations of body shapes with insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk in middle-aged and elderly Chinese, Nutrition & Metabolism14 Jul 2023
Associations of body shapes with insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk in middle-aged and elderly Chinese, Nutrition & Metabolism14 Jul 2023 Fashion, Beauty, Body Positivity, Lifestyle14 Jul 2023
Fashion, Beauty, Body Positivity, Lifestyle14 Jul 2023
You may also like
 No Boundaries Juniors' Color Pop Triangle Lace Bralette14 Jul 2023
No Boundaries Juniors' Color Pop Triangle Lace Bralette14 Jul 2023 Women's Nike Black Seattle Seahawks Yard Line Crossover Leggings14 Jul 2023
Women's Nike Black Seattle Seahawks Yard Line Crossover Leggings14 Jul 2023 Ladies Tracksuit Long Sleeve Jacket Knee Ripped Zip Hooded Tracksuit Women Tracksuits Long Sleeve Coat Knee Hole Zipper Hooded Sports Suit14 Jul 2023
Ladies Tracksuit Long Sleeve Jacket Knee Ripped Zip Hooded Tracksuit Women Tracksuits Long Sleeve Coat Knee Hole Zipper Hooded Sports Suit14 Jul 2023 Women's Maidenform DM7680 Pure Comfort Lace Push-Up Wireless Bra (Black 2X)14 Jul 2023
Women's Maidenform DM7680 Pure Comfort Lace Push-Up Wireless Bra (Black 2X)14 Jul 2023 Buy Fabluk® Elite Performance Zip-Front Sports Bra Longline, Supportive Workout & Yoga Top with Enhanced Comfort with Free Bella VOSTE Eye Makeup Combo (Black, M) at14 Jul 2023
Buy Fabluk® Elite Performance Zip-Front Sports Bra Longline, Supportive Workout & Yoga Top with Enhanced Comfort with Free Bella VOSTE Eye Makeup Combo (Black, M) at14 Jul 2023 Active Yoga Pants in Moose – SistersandSeekers14 Jul 2023
Active Yoga Pants in Moose – SistersandSeekers14 Jul 2023 Sale: Faux Leather Square Neck Dress14 Jul 2023
Sale: Faux Leather Square Neck Dress14 Jul 2023 Brooks Brothers, Accessories, Brooks Brothers Leather Red Blue Striped Suspenders Made In Usa Brass Braces14 Jul 2023
Brooks Brothers, Accessories, Brooks Brothers Leather Red Blue Striped Suspenders Made In Usa Brass Braces14 Jul 2023 Men's Boxers Under Armour Charged Tech 6in 2 Pack - black/red14 Jul 2023
Men's Boxers Under Armour Charged Tech 6in 2 Pack - black/red14 Jul 2023 Honeylove® · Where function meets fashion14 Jul 2023
Honeylove® · Where function meets fashion14 Jul 2023