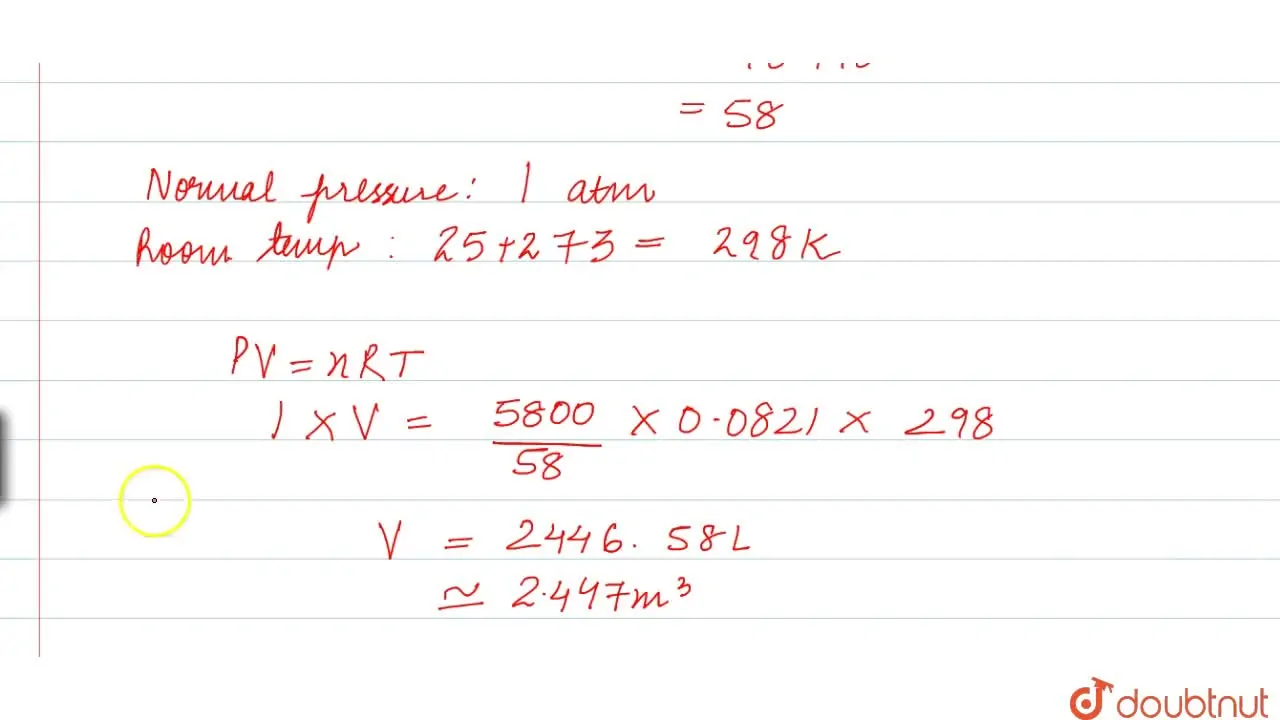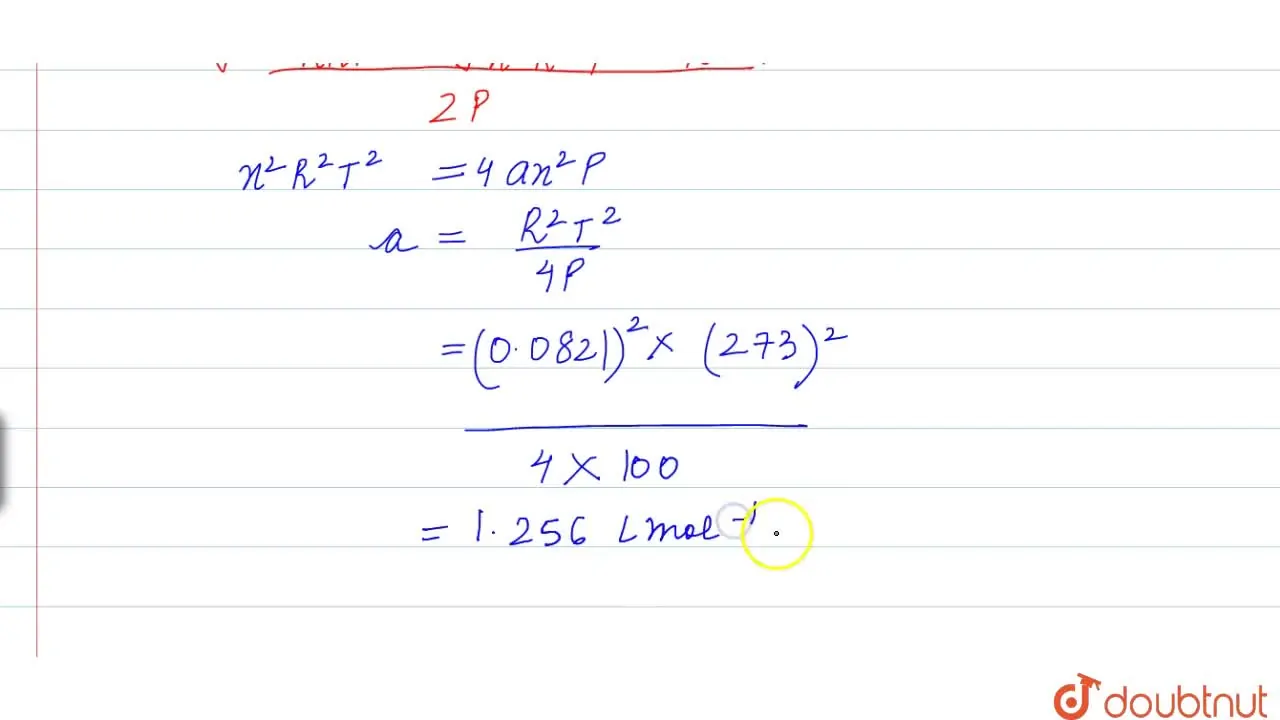The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 25 Sept 2024

For 1 mol of a gas, the van der Waals equation is (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))(V(m)-b)=RT Ignoring b, we get (given volume of gas molecule is negligible) (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))V(m)=RT ltbgt or pV(m)+(a)/(V(m))=RT or (pV(m))/(RT)+(a)/(V(m)RT)=1 or Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=1-(a)/(V(m)RT) (i) It is given that Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=0.5implies V(m)=(0.5RT)/(P) With this, equation (i) becomes 0.5=1-(a)/((0.5RT//p)RT) or a=(0.5)((0.5RT)/(p))RT=0.25(R^(2)T^(2))/(p) Substiuting the given values, we get a=(0.25)[((0.082L atm K^(-1)mol^(-1))^(2)(273 K)^(2))/((100 atm))] =1.2528 L^(2) atm mol^(-2)
An LPG cylinder weighs 14.8 kg when empty. When full it weighs 29.0 kg
The ratio of rate of diffusion of gases A and B is 1:4 and their molar
Two reactants A and B separately shows two chemical reactions.Both rea
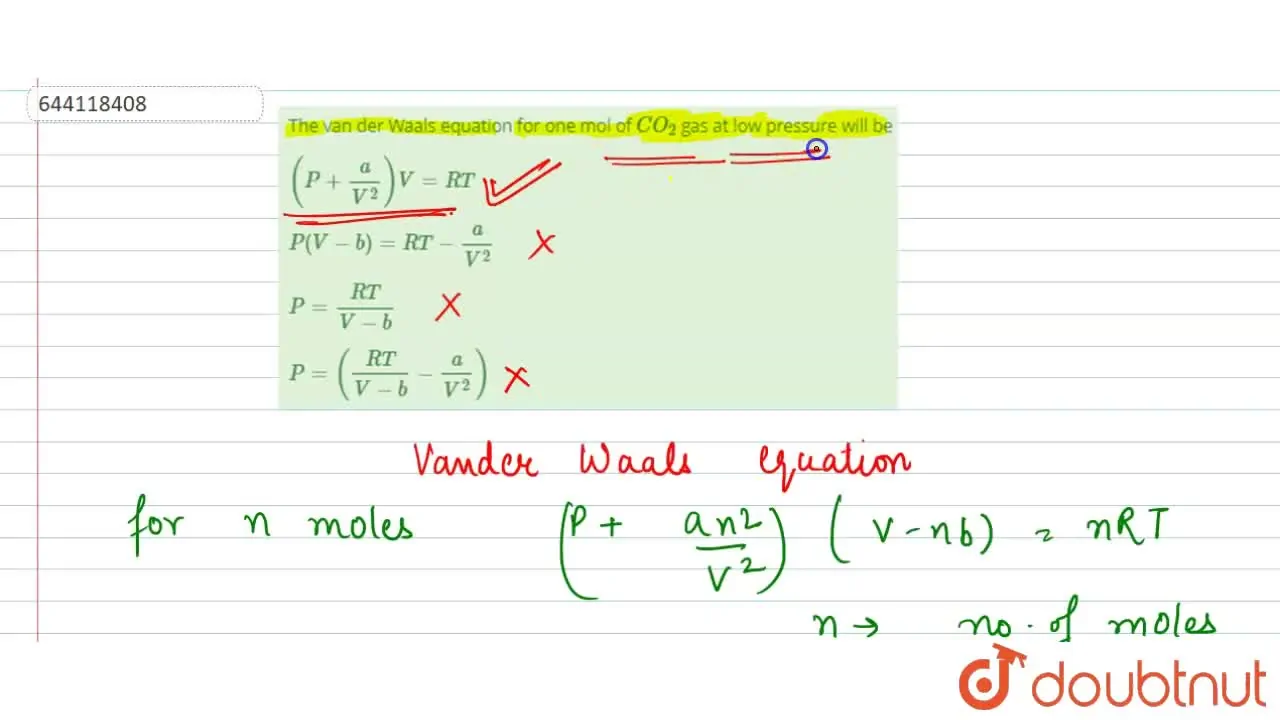
The van der Waals equation for one mol of CO(2) gas at low pressure wi
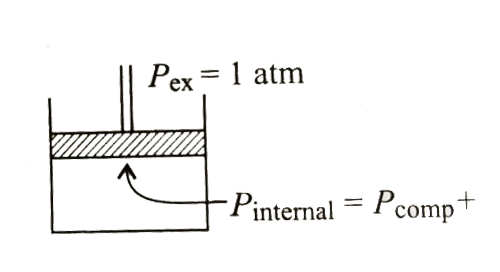
To an evacuated vessel with movable piston under external pressure of
Which of the following equations represents the compressibility factor
To an evacuated vessel with movable piston under external pressure of
The compressibility factor for definite amount of van der Waals' gas a
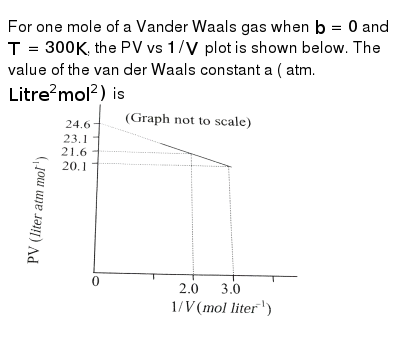
For one mole of a van der Waals' gas when b=0 and T=300K, the pV vs 1/
An evacuated glass vessel weighs 50.0 g when empty, 148.0 g when fille
The absolute temperature of an ideal gas is….. to/than the average kin
Recommended for you
- At Critical Temperature,pressure and volume . The compressibility Factor (Z) Is14 Jul 2023
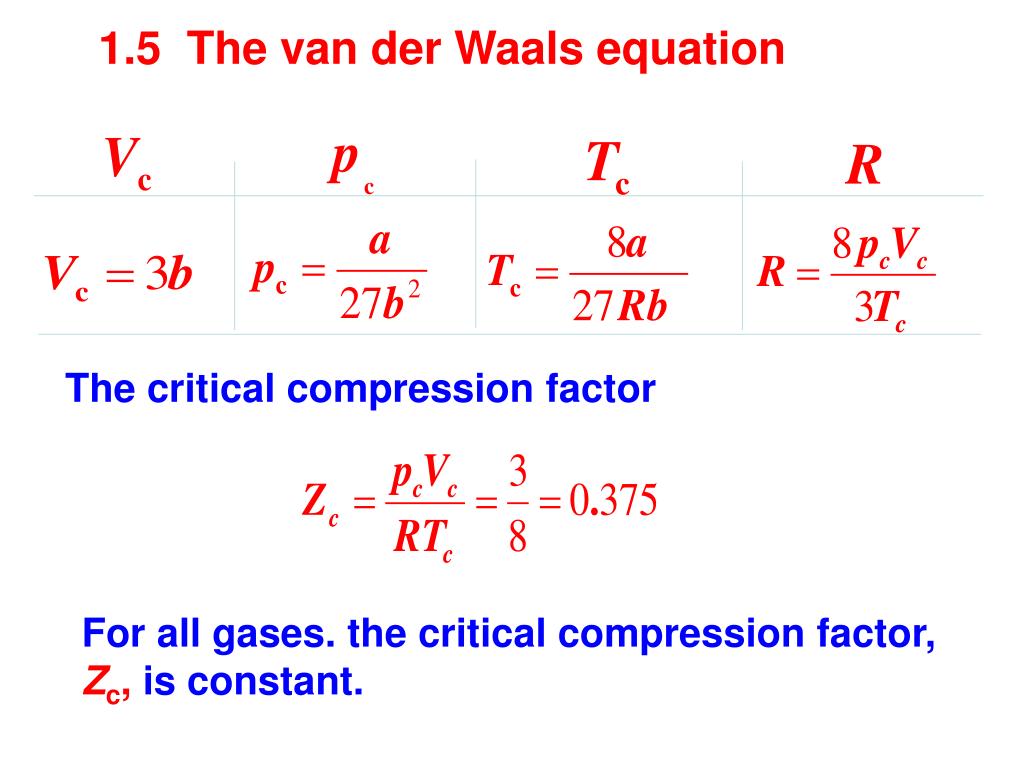 PPT - Real gases PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:395949114 Jul 2023
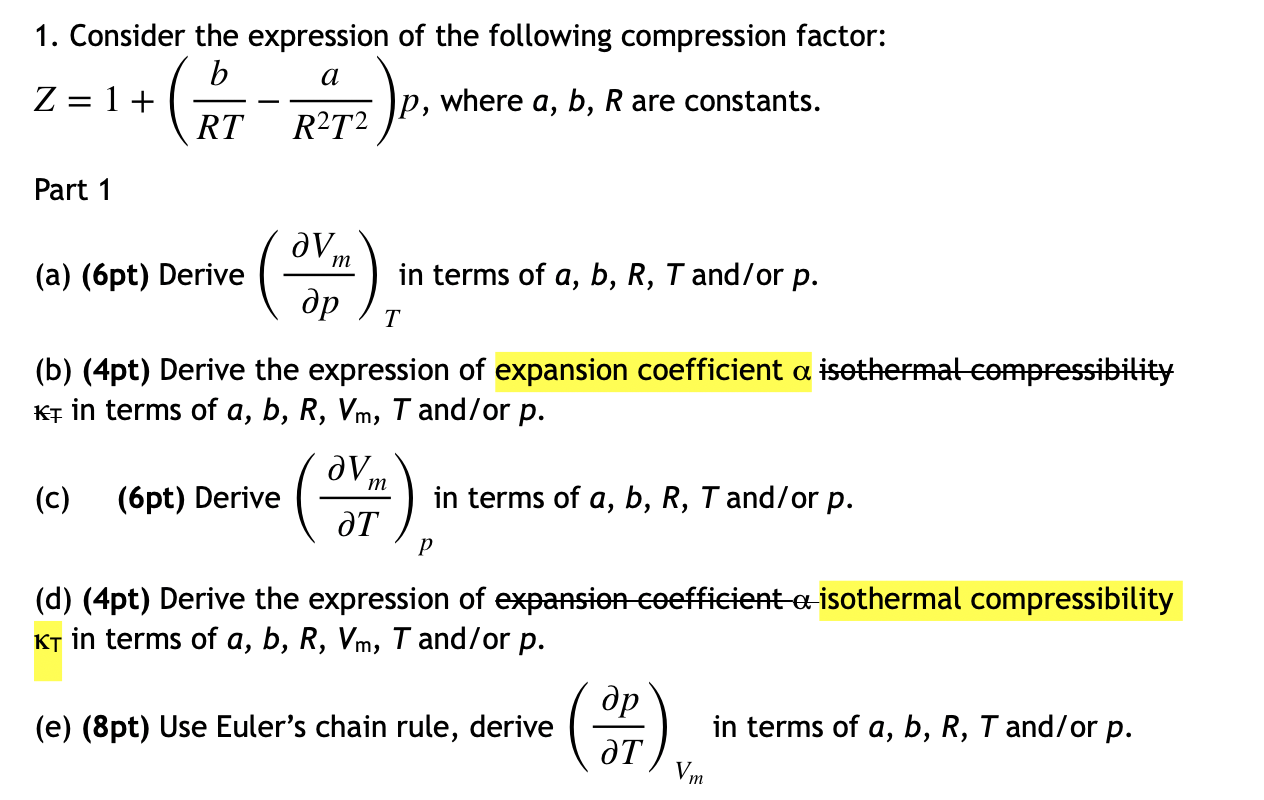
PPT - Real gases PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:395949114 Jul 2023- Solved 1. Consider the expression of the following14 Jul 2023
- Answer in General Chemistry for Carl #27553314 Jul 2023
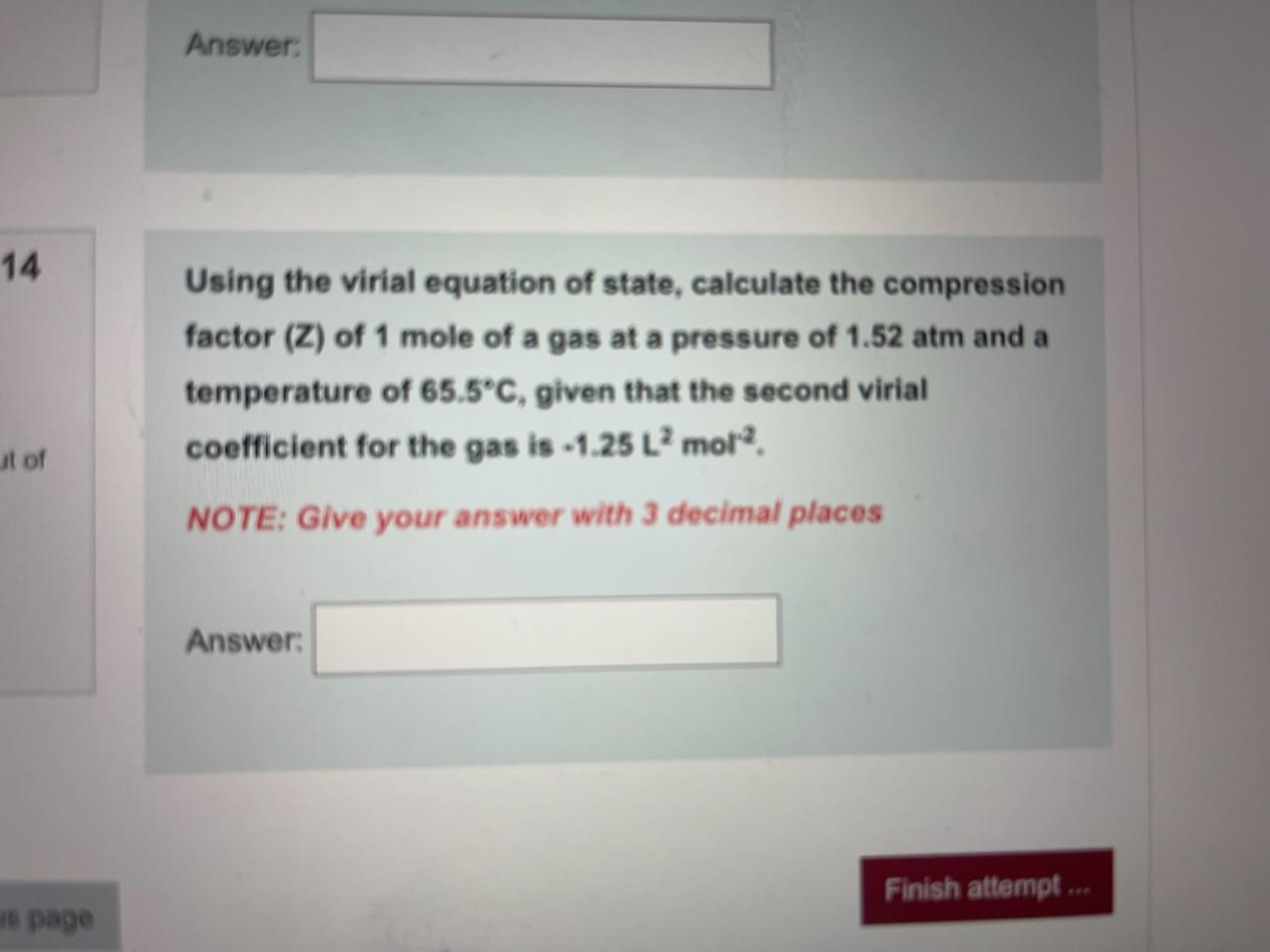
- Solved Using the virial equation of state, calculate the14 Jul 2023
- Solved Define the compression factor, Z and explain its14 Jul 2023
 At a given temperature T gases Ne Ar Xe and Kr are found to deviate from ideal gas behavior (JEE MAINS 2019) - Doctor Logics Sunny Garg Chemistry14 Jul 2023
At a given temperature T gases Ne Ar Xe and Kr are found to deviate from ideal gas behavior (JEE MAINS 2019) - Doctor Logics Sunny Garg Chemistry14 Jul 2023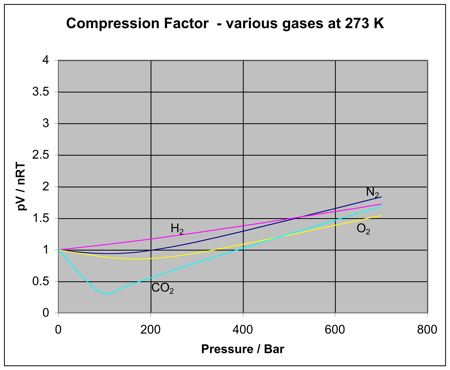 Non-ideal behavior of gases (article)14 Jul 2023
Non-ideal behavior of gases (article)14 Jul 2023 SOLVED: Derive an expression for the compression factor of a gas14 Jul 2023
SOLVED: Derive an expression for the compression factor of a gas14 Jul 2023 53 pts!! The function f(x)= 7^x+1 is transformed to function g14 Jul 2023
53 pts!! The function f(x)= 7^x+1 is transformed to function g14 Jul 2023
You may also like
 Puff Sleeve Denim Corset Top – FEHRNVI14 Jul 2023
Puff Sleeve Denim Corset Top – FEHRNVI14 Jul 2023 Plus Size Active Wear Jacket14 Jul 2023
Plus Size Active Wear Jacket14 Jul 2023 Sexy Set Logirlve Sexy Push Up Bralette And Panty Set Plus Size14 Jul 2023
Sexy Set Logirlve Sexy Push Up Bralette And Panty Set Plus Size14 Jul 2023 Bombas mens bee better - Gem14 Jul 2023
Bombas mens bee better - Gem14 Jul 2023 Under Armour Women's Ua Hg Armour Mid Padless Bra, Midnight Navy14 Jul 2023
Under Armour Women's Ua Hg Armour Mid Padless Bra, Midnight Navy14 Jul 2023 THE NORTH FACE Anchor 1/4 Zip Mens Fleece14 Jul 2023
THE NORTH FACE Anchor 1/4 Zip Mens Fleece14 Jul 2023 Cotton Lycra Churidar Free Size Skin Leggings14 Jul 2023
Cotton Lycra Churidar Free Size Skin Leggings14 Jul 2023 POLO RALPH LAUREN Mens Rugby Polo Shirt Size 3XB Blue Green Striped Crest NWT $151.25 - PicClick AU14 Jul 2023
POLO RALPH LAUREN Mens Rugby Polo Shirt Size 3XB Blue Green Striped Crest NWT $151.25 - PicClick AU14 Jul 2023- Stradivarius seamless ribbed leggings in black14 Jul 2023
 KNIX padded v-neck evolution bra14 Jul 2023
KNIX padded v-neck evolution bra14 Jul 2023