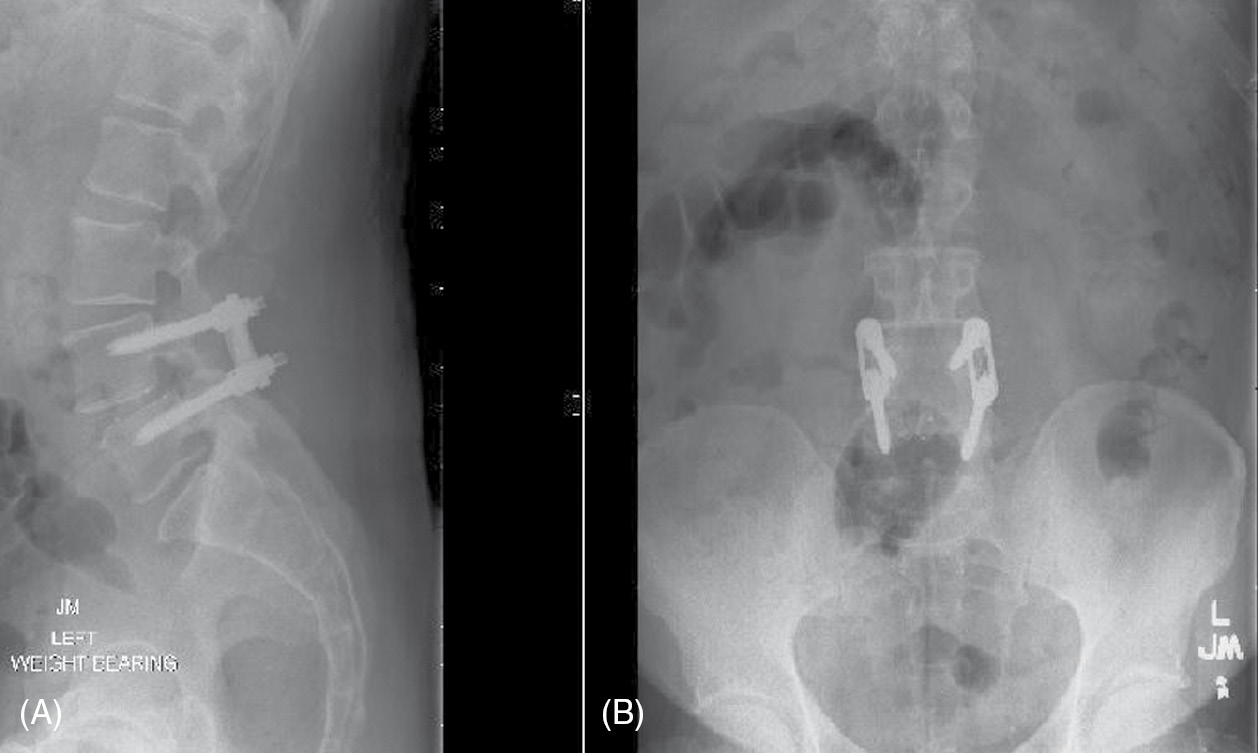
Continuously expandable interbody spacer in (A) minimized and (B)
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 21 Sept 2024

Download scientific diagram | Continuously expandable interbody spacer in (A) minimized and (B) expanded forms (RISE-L Globus Medical, Inc, Audubon, PA). from publication: Comparative Effectiveness of Expandable Versus Static Interbody Spacers via MIS LLIF: A 2-Year Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes Study | Study Design Retrospective cohort study. Objective The purpose of this study is to compare the radiographic and clinical outcomes of expandable interbody spacers to static interbody spacers. Methods This is a retrospective, institutional review board–exempt chart review of | Static, Mullerian Inhibiting Substance (MIS) and Outcome Assessment (Health Care) | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with an expandable interbody device: Two-year clinical and radiographic outcomes - North American Spine Society Journal (NASSJ)
Surgical techniques (Chapter 8) - Anesthesia for Spine Surgery
Static interbody spacer (TransContinental, Globus Medical, Inc
A and B) Immediate postoperative AP and lateral images of the above
Show the model of BAN Figure 3 shows the scenario of normal nodes with
FlareHawk9 – Accelus
Yan Michael LI, MD PhD, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Texas, MD Anderson
Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic and open posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of single-segmental lumbar degenerative diseases, BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders
Charles LEDONIO, Senior Director, Exactech, Inc., Florida, Clinical Affairs
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with an expandable interbody device: Two-year clinical and radiographic outcomes - North American Spine Society Journal (NASSJ)
Recommended for you
 A Thermal Spacer: Reducing Point Thermal Bridges in Rainscreen Assemblies — D.TO: Design TOgether14 Jul 2023
A Thermal Spacer: Reducing Point Thermal Bridges in Rainscreen Assemblies — D.TO: Design TOgether14 Jul 2023 Overlay Reducing Spacer14 Jul 2023
Overlay Reducing Spacer14 Jul 2023- 💥New ~ SpaceOAR Vue Hydrogel Spacer Procedure (for prostate CA) from the Vargo Anesthesia Mega App. - An outpatient procedure in which14 Jul 2023
 Coe Disposable Spacer Trays14 Jul 2023
Coe Disposable Spacer Trays14 Jul 2023 Capezio Spacers - SOLEUS DANCE & FITNESS WEAR14 Jul 2023
Capezio Spacers - SOLEUS DANCE & FITNESS WEAR14 Jul 2023 Simpson SBR/43-R20 Structural Spacer Bracers - G90 Galvanized (box14 Jul 2023
Simpson SBR/43-R20 Structural Spacer Bracers - G90 Galvanized (box14 Jul 2023 Throttle Body Spacer for Daihatsu Atrai S320G S330G EF-DET JB-DET14 Jul 2023
Throttle Body Spacer for Daihatsu Atrai S320G S330G EF-DET JB-DET14 Jul 2023 ♢ Sonic MS Verstraβe Motorsport Technik Wheel Spacers for BMW14 Jul 2023
♢ Sonic MS Verstraβe Motorsport Technik Wheel Spacers for BMW14 Jul 2023 Square Bore Carb Spacer, Reduce Fuel Temperature14 Jul 2023
Square Bore Carb Spacer, Reduce Fuel Temperature14 Jul 2023 Does spiked tibial cement spacer reduce spacer-related problems in two-stage revision total knee arthroplasty for infection?14 Jul 2023
Does spiked tibial cement spacer reduce spacer-related problems in two-stage revision total knee arthroplasty for infection?14 Jul 2023
You may also like
 Best white Heavy Duty Sewing Machine for sale in Lawrenceville14 Jul 2023
Best white Heavy Duty Sewing Machine for sale in Lawrenceville14 Jul 2023 Women Silk Bra, 100% Mulberry Silk, Large Sizes Available, T-shit Bra, Yoga/pilates/exersize Bra, Sleeping Bra14 Jul 2023
Women Silk Bra, 100% Mulberry Silk, Large Sizes Available, T-shit Bra, Yoga/pilates/exersize Bra, Sleeping Bra14 Jul 2023 Feel Good and Discover Your Perfect Bra Size14 Jul 2023
Feel Good and Discover Your Perfect Bra Size14 Jul 2023 Seven ways to lose weight with minimal effort, according to science14 Jul 2023
Seven ways to lose weight with minimal effort, according to science14 Jul 2023 HIGH TEMP POWDER COATING PLUGS, CAPS AND KITS14 Jul 2023
HIGH TEMP POWDER COATING PLUGS, CAPS AND KITS14 Jul 2023- Genuine leather belt for women. Wide leather belt. Handmade.14 Jul 2023
- What is she thinking about? 😍 Leather leggings 👉 LINK IN BIO! 🖤 @lalelookcom Model: @satinva14 Jul 2023
 Rossignol Midlayers & Base Layers14 Jul 2023
Rossignol Midlayers & Base Layers14 Jul 2023 Saree Shapewear - The online shopping beauty store. Shop for14 Jul 2023
Saree Shapewear - The online shopping beauty store. Shop for14 Jul 2023 Basketball Compression Pants with Knee Pads Capri Protector Gear14 Jul 2023
Basketball Compression Pants with Knee Pads Capri Protector Gear14 Jul 2023