Real Gases. The ideal gas equation of state is not sufficient to describe the P,V, and T behaviour of most real gases. Most real gases depart from ideal. - ppt download
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 22 Sept 2024

Most real gases depart from ideal behaviour at deviation from low temperature high pressure.
High positive potential energy (little separation) Repulsive interactions Intermediate separations attractive interactions dominate Large separations (on the right) the potential energy is zero and there is no interaction between the molecules..
Real gas molecules do attract one another (P id = P obs + constant) Real gas molecules are not point masses (V id = V obs - const.)
V id = V obs - nb b is a constant for different gases P id = P obs + a (n / V) 2 a is also different for different gases Ideal gas Law P id V id = nRT
Critical temperature (T c ) - the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied Critical pressure (P c ) – the minimum pressure that needs to be applied at T c to bring about liquefaction
For a perfect gas, the slope is zero Boyle temperature the slope is zero and the gas behaves perfectly over a wider range of conditions than at other temperatures.
Boyle temperature - for a van der Waal s gas, the Boyle temperature (T B ) is written
The reduced state variables are defined
Re-write the Van der Waals in terms of reduced variables
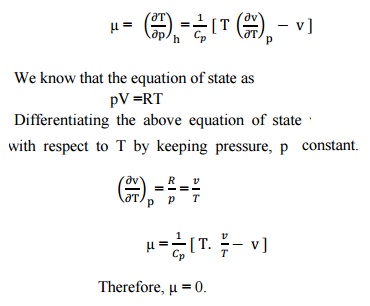
The chemical potential of a real gas is written in terms of its fugacity
In gaseous systems, we relate the fugacity (or activity) to the ideal pressure of the gas via.
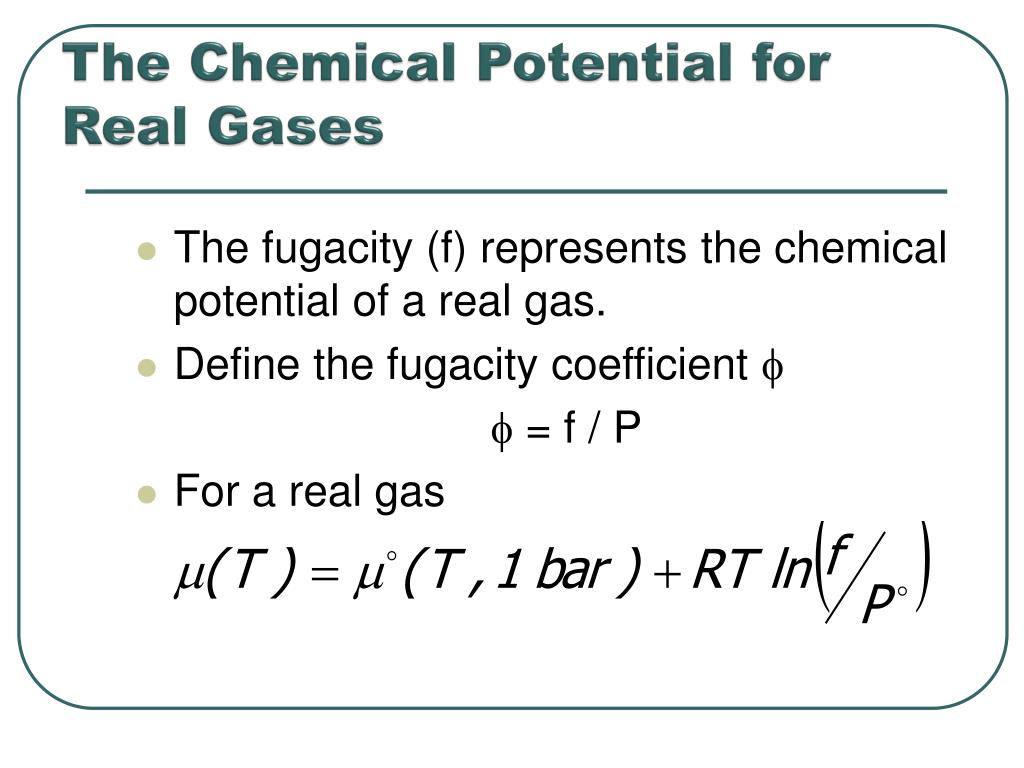
Define the fugacity coefficient = f / P For a real gas.
Comparing the chemical potential of the real gas to the chemical potential of an ideal gas at the same pressure
The fugacity coefficients are obtained from the compression factors (Z) as shown below
High positive potential energy (little separation) Repulsive interactions Intermediate separations attractive interactions dominate Large separations (on the right) the potential energy is zero and there is no interaction between the molecules..
Real gas molecules do attract one another (P id = P obs + constant) Real gas molecules are not point masses (V id = V obs - const.)
V id = V obs - nb b is a constant for different gases P id = P obs + a (n / V) 2 a is also different for different gases Ideal gas Law P id V id = nRT
Critical temperature (T c ) - the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied Critical pressure (P c ) – the minimum pressure that needs to be applied at T c to bring about liquefaction
For a perfect gas, the slope is zero Boyle temperature the slope is zero and the gas behaves perfectly over a wider range of conditions than at other temperatures.
Boyle temperature - for a van der Waal s gas, the Boyle temperature (T B ) is written
The reduced state variables are defined
Re-write the Van der Waals in terms of reduced variables
The chemical potential of a real gas is written in terms of its fugacity
In gaseous systems, we relate the fugacity (or activity) to the ideal pressure of the gas via.
Define the fugacity coefficient = f / P For a real gas.
Comparing the chemical potential of the real gas to the chemical potential of an ideal gas at the same pressure
The fugacity coefficients are obtained from the compression factors (Z) as shown below
REAL VS IDEAL GASES. Ideal Gases Ideal gas may be defined as a gas which obeys the gas equation (PV=nRT) under all conditions of temperature and pressure; - ppt download
Chemistry 231 Real Gases. The ideal gas equation of state is not sufficient to describe the P,V, and T behaviour of most real gases. Most real gases depart. - ppt download
Important Questions and Answers: Ideal And Real Gases, Thermodynamic Relations
Ideal & real gases
Real Gases. The ideal gas equation of state is not sufficient to describe the P,V, and T behaviour of most real gases. Most real gases depart from ideal. - ppt download
Liquefaction of Gases - GeeksforGeeks
Real vs Ideal Gases - Wize University Chemistry Textbook
PPT - Chemistry 231 PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:967425
Real Gases. The ideal gas equation of state is not sufficient to describe the P,V, and T behaviour of most real gases. Most real gases depart from ideal. - ppt download
Joule Thomson Effect Definition - Joule Thomson Coefficient
Recommended for you
 How to Calculate Compression Ratio: 9 Steps (with Pictures)14 Jul 2023
How to Calculate Compression Ratio: 9 Steps (with Pictures)14 Jul 2023- Solved 6. Let's see if we can derive an alternative14 Jul 2023
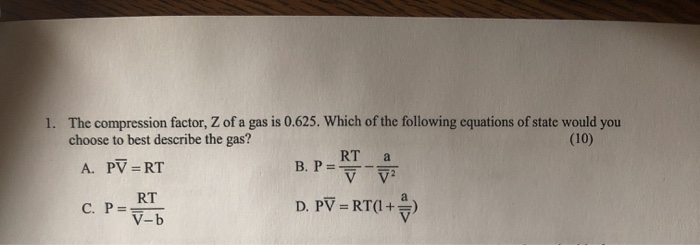 Solved 1. The compression factor, Z of a gas is 0.625. Which14 Jul 2023
Solved 1. The compression factor, Z of a gas is 0.625. Which14 Jul 2023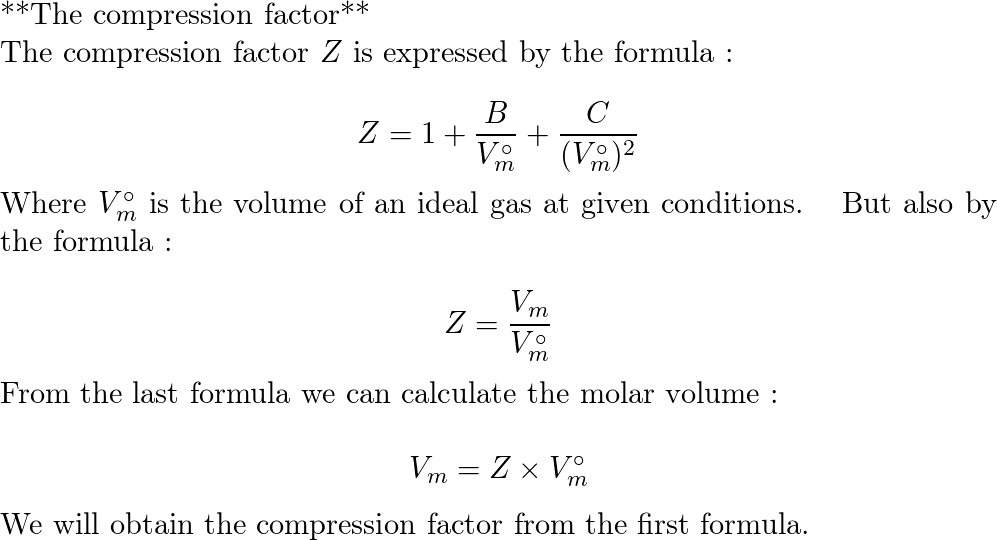 At 273 K measurements on argon gave B = -21.7 cm$^3$ mol$^{14 Jul 2023
At 273 K measurements on argon gave B = -21.7 cm$^3$ mol$^{14 Jul 2023 UNUB At Boyle temperature, the value of compressi factor Z has a value of one over a wide range of pressure. This is due to the fact that in the van der14 Jul 2023
UNUB At Boyle temperature, the value of compressi factor Z has a value of one over a wide range of pressure. This is due to the fact that in the van der14 Jul 2023 Write an equation for the transformation of y=x vertical compression by a factor of 1/1114 Jul 2023
Write an equation for the transformation of y=x vertical compression by a factor of 1/1114 Jul 2023 What is the value of compression factor Z for the gas? (A) 1 (B) >1 (C) <1 (D) Zero14 Jul 2023
What is the value of compression factor Z for the gas? (A) 1 (B) >1 (C) <1 (D) Zero14 Jul 2023 Find the isothermal compressibility `x` of a Van der Walls gas as a function of volume14 Jul 2023
Find the isothermal compressibility `x` of a Van der Walls gas as a function of volume14 Jul 2023 At a given temperature T gases Ne Ar Xe and Kr are found to deviate from ideal gas behavior (JEE MAINS 2019) - Doctor Logics Sunny Garg Chemistry14 Jul 2023
At a given temperature T gases Ne Ar Xe and Kr are found to deviate from ideal gas behavior (JEE MAINS 2019) - Doctor Logics Sunny Garg Chemistry14 Jul 2023 Find the isothermal compressibility `x` of a Van der Walls gas as14 Jul 2023
Find the isothermal compressibility `x` of a Van der Walls gas as14 Jul 2023
You may also like
 Womens Bras in Womens Bras14 Jul 2023
Womens Bras in Womens Bras14 Jul 2023 Beheizbare Unterwäsche als Alltagslösung von - Industrie und Forschung14 Jul 2023
Beheizbare Unterwäsche als Alltagslösung von - Industrie und Forschung14 Jul 2023 LADY LUXE, A crystal wedding headband for bride Jessica - TANIA MARAS14 Jul 2023
LADY LUXE, A crystal wedding headband for bride Jessica - TANIA MARAS14 Jul 2023 Gilbin Ultra Soft High Waist Yoga Stretch Mini-Bike Shorts for Women-Many Colors-One Size & Plus Size (Tan S-L)14 Jul 2023
Gilbin Ultra Soft High Waist Yoga Stretch Mini-Bike Shorts for Women-Many Colors-One Size & Plus Size (Tan S-L)14 Jul 2023 Girls Athletic Yoga Pants Size 11-12 Years Old Shiny Black Stretchy Fashion Bright Pants For Teens Kids Running Casual14 Jul 2023
Girls Athletic Yoga Pants Size 11-12 Years Old Shiny Black Stretchy Fashion Bright Pants For Teens Kids Running Casual14 Jul 2023 Butt Lifter Panties, Plus Size Women Tummy Control Panties Butt14 Jul 2023
Butt Lifter Panties, Plus Size Women Tummy Control Panties Butt14 Jul 2023 DOMIKING Pink Crown Womens Underwear Stretch Bikini Panties Soft Briefs for Women Girl Teen XS, Multicolor, X-Small : : Clothing, Shoes & Accessories14 Jul 2023
DOMIKING Pink Crown Womens Underwear Stretch Bikini Panties Soft Briefs for Women Girl Teen XS, Multicolor, X-Small : : Clothing, Shoes & Accessories14 Jul 2023 MOS on X: \ BIG NEWS‼️/ Finally, it will be broadcast tomorrow 👏. Don't miss it on Tuesday, July 11 at 20:00‼️ See you on NBC #AGT 💪🔥. Enjoy the MOS performance! #14 Jul 2023
MOS on X: \ BIG NEWS‼️/ Finally, it will be broadcast tomorrow 👏. Don't miss it on Tuesday, July 11 at 20:00‼️ See you on NBC #AGT 💪🔥. Enjoy the MOS performance! #14 Jul 2023 Buy Enamor Girlies Black Full Coverage Lace Bra FF07 - Bra for Women 65060314 Jul 2023
Buy Enamor Girlies Black Full Coverage Lace Bra FF07 - Bra for Women 65060314 Jul 2023- ASOS 4505 Icon yoga legging14 Jul 2023